Testing team plays an essential role in defining the success of a particular software product. Team composition specifies in different ways – in many companies and even in each project. The same regarding organizational structure. Software testing role distribution depends on the project’s specific as well as testing budget. But along with this – team location, knowledge, skills and practical experience in software testing. Leading elements that influence may change over time.
Given the above, the testing team possible consist of one single general QA engineer or many QA professionals who perform different software testers’ tasks and have various responsibilities within particular skills. They all work together to achieve the overall objective of the project’s business through testing.
On the other hand, quality is the responsibility of each project participant not only testing team members. All stakeholders should be interested in a quality product, including – the Development team (Devs), Project management team (PM, PO), and team responsible for gathering, processing and testing requirements.
One full-stack software test engineer or, in other words, general software tester cannot test big products alone because it is very resource-consuming. Also, full-stack testers are inferior to niche QA engineers when causing the need for highly specialized knowledge.
However, the role of general QA engineers is quite in demand in the worldwide software testers professionals market. Whether it’s an outsourcing or outstaffing company, a company that offers software testing services or consulting. Additionally, general QA engineers can be in-house or a part of a remote QA company.
Ideal size for QA team
The ideal size depends on… but what? Topic of how many members are in a QA team is old. Follow the link to meet the top answers on StackExchange. The organizer of this discussion complained that with the growth of his team, overall team productivity was down. So, he asked for advice. There detected clarifications of at least 3 test engineers and up to 10-12 for high-scaled projects. But all participants agreed that there is no universal formula for an effective QA team, especially an Agile testing team.
Different Roles and Responsibility In The Quality Assurance Team
Normally, the following members compose a functional software testing team ⬇️ 👉 Let’s briefly look at their QA roles and job responsibilities they typically handle in the testing process!
Popular Software testing Roles & Responsibilities
| Quality Control Engineer (QC) | The term comes from the manufacturing industry. QC in the software industry is responsible for testing new products and determining whether those products meet business requirements in reliability and functionality. Implements the test program established by QA procedures, testing efforts are concentrated on finding defects. |
| Quality Assurance Engineer (QA) | Determines test procedures that can enable to test of a particular software app in the beat particular manner. Designing test suites, create test cases and test documentation. Executes all levels of testing. Run tests according to the test standards within various testing techniques. Analyzes and reports test results. To help troubleshoot errors, before the product will be pushed into production. |
| Test Analyst | Focuses on the business problem. Should have the ability to see the big picture, good planning and organizational skills. Analyzes requirements and acceptance criteria, designes software testing documentation including test plans, links tests to req, run tests, analyzes and documents results. |
| Test Consultant | Involved in all (SDLC) phases of an IT project where they can improve all needed aspects of software development. They ought to be interested in the current trend in software development (including Agile and DevOps). Should own an analytical mindset and of course excellent communication skills. |
| Test Automation Engineer (AQA) | Primarily is focused on coding test framework and then quality. Set up a test environment, and develops test scripts using the testing tools like Selenium, Codecept or others to design and run automated test cases. |
| Test Architect | Works with the project infrastructure, prepares test strategy and implements test automation tools to support product code and test code. Sometimes performs low-level testing like unit testing, module testing, performance testing, acceptance testing. Should have strong knowledge of backend services. |
| Test Manager | QA manager acts a little like a project manager. Design test strategy, organize test processes, track test progress and supervises the teamwork through test planning. |
| Director of test | One senior manager who manages Test managers. Should set QA strategy and approach for all the company`s products and be ultimately responsible for quality. Guarantee the success of manual and automation testing efforts of all testing teams in the organization. |
Moreover, many modern Agile QA teams are even more diverse. There may be several QA engineers, Test Analysts, Requirement Analysts, Test Architects, Test Managers, QA Team Lead and other QA roles. Sometimes they divide their authority and responsibilities with each other to the stage of the software development process.
Tiny teams don’t always have test automation engineers. Even more unique is the role of an Automation Test Architect, typically, this professional switches from SDET or backend development roles. Otherwise, the roles are hired QA consultants, likely experienced Automation QA consultants. The same Performance testers (carry load and stress tests), Security QA, Network test engineer, DevOps, Usability software tester, Accessibility test professional, Scrum master, release manager etc.
A manual QA engineer, except the writing of test cases, execution of manual tests and their maintenance, can partially or completely perform the role of a QA analyst or QA coordinator. QA coordinator alternatively plays the Project manager role in the project. Regarding QC, they handle the execution of manual testing only.
The demand for the QA architect and DevOps is more noticeable in big companies with complex infrastructures.
The outsourcing QA teams can balance business requirements, testing and delivery in several projects, what’s much more tricky!
Nevertheless, test team members must know what is expected of each. They should know their role and responsibilities, clearly understand who is in charge and what to expect from their team. Commonly, this occurs through the Team agreement document where all parties involved come to a consensus.
A team agreement, often called a team charter or contract, is a document created by a development team to establish shared expectations, norms, and guidelines for working together effectively. It might be an informal agreement or a structured written document.
A team agreement outlines the team’s purpose, goals, roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, decision-making processes, and conflict-resolution strategies. A team agreement serves as a foundational document that helps to align team members, foster collaboration, and mitigate misunderstandings or even conflicts. It promotes transparency and accountability among the Agile team, ultimately contributing to the team’s success in achieving its objectives.
Why QAs tend to deep their technical skills in test automation?
Let’s consider why QAs often seek to enhance their technical skills in automation and not deeper into management instead.
Several software testing industry reasons impact:
Firstly, automation allows for the efficient execution of repetitive and time-consuming tasks, freeing up QAs time for more strategic and high-value activities.
Secondly, automated tests enable testing quicker and more accurate, enhancing the overall efficiency of the testing process.
Thirdly, proficiency in automation tools aligns with the popular trends in software testing methodologies towards Agile and DevOps methodologies, where rapid CI\CD is essential.
As such, by deepening their technical skills in automation, QAs can stay competitive in the landscape of software development and quality assurance and earn higher salaries.
What do you think about these titles?
- Principal QA Engineer
- VP Engineer
- Transformation manager
- Managing Director
- Engineering Manager
Let’s dive in briefly into these job descriptions!
Pay attention to the most valued opinions as answers to our open discussion:
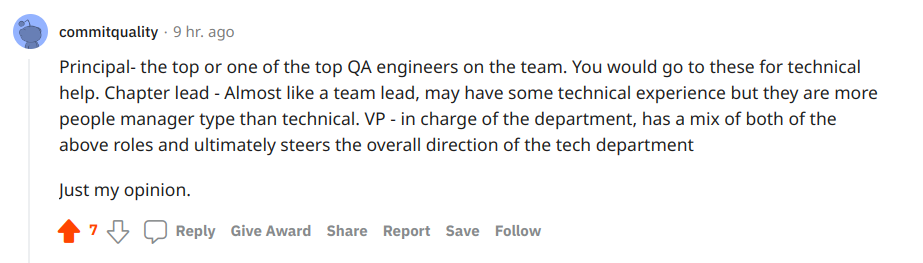
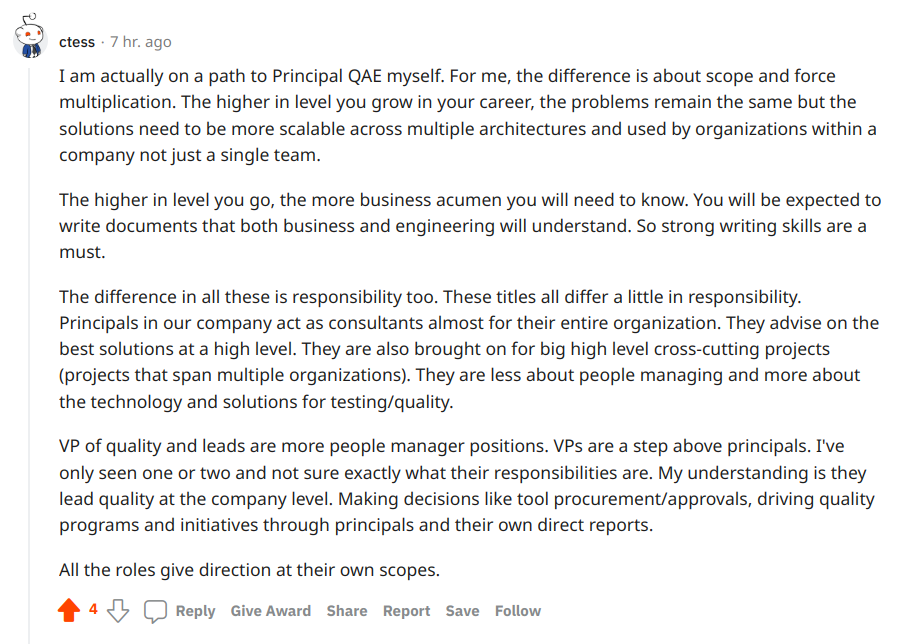
👉 Come on follow through link and join our testomatio Reddit discussion
Who participates in Quality Assurance Team Building
Building and managing a high-performance Agile test team that provides business value to the organization is one of the most complicated tasks in test management. Besides, the QA manager, as well HR manager, talent equitation manager, CEO and CTO participate in team organization. They are reviewing candidates in terms of their duties.
In order to create a capable testing team, they outline the software testing team structure, might assign software testing team responsibilities, and define software testing team objectives. The primary goal is to keep the project on track.
The essence of the Agile Software testing team
One more time saying, TEAM – Together Everyone Achieves More. This means Agile at first, is a team-orientated approach as well as a customer-orientated approach.
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools.
- Working software over comprehensive documentation.
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan.
And the next 12 Agile principles are:
- Satisfying customers through early and continuous delivery of valuable work.
- Breaking big work down into smaller tasks that can be completed quickly.
- Recognizing that the best work emerges from self-organized teams.
- Providing motivated individuals with the environment and support they need and trusting them to get the job done.
- Creating processes that promote sustainable efforts.
- Maintaining a constant pace for completed work.
- Welcoming changing requirements, even late in a project.
- Assembling the project team and business owners on a daily basis throughout the project.
- Having the team reflect at regular intervals on how to become more effective, then tuning and adjusting behavior accordingly.
- Measuring progress by the amount of completed work.
- Continually seeking excellence.
- Harnessing change for a competitive advantage.
The Role Of Quality Assurance (QA) In Development
In Agile SDLC, testing starts in the early stages of software development, so development and testing processes are simultaneous. And as a result, testers are closely integrated into each stage of the Agile Software Development Life Cycle.
QA Engineers’ involvement helps to optimize the risks and create alignment. They create all possible test scenarios. QA test analyst check the business requirements for inconsistencies or logical gaps in functionality. The test team closely interact with the Dev team and customer, being a kind of bridge between them.
The Role Of Quality Assurance (QA) In Deployment
The role of Quality Assurance (QA) in deployment consists of that QA is on standby during a deployment. As soon as the release goes live, QA gets to work, undergoing smoke testing to ensure that the deployment went smoothly.
After that, the testing team repeats the stages mentioned above over and over again during the product life cycle – regression testing. They check new features, find new bugs during regular software inspection, and analyze bugs reported by users.
QAs check all of the product features by way of finding and reporting bugs and estimating overall product quality. Testers have the power to approve software for release or send code to rework. The decision depends on the number of critical bugs.
The Role Of Quality Assurance (QA ) In Maintenance
Bugs do occasionally slip through, even the best automation or manual testing cannot find all the bugs. QA must be on hand to test the feature updates or bug fixes.
Factors influencing QA team performance:
- effective communication
- engagement
- strong collaboration daily.
- knowledge transfering
These traits are essential in synergy testing efforts that influence on the end product quality.
Sharing of experience, mentoring, coaching, training and team building are also important in growing effectiveness within an Agile testing team.
What Characterizes a Successful Software Quality Assurance Engineer?
In conclusion, the roles and responsibilities of a Quality Assurance (QA) Engineer are varied and complex. This role is crucial in resulting in customer satisfaction.
The QA roles require a deep understanding of the software development process and test design methodologies. They should exhibit keen attention to detail and be proficient in some technical aspects, especially related to popular testing tools like Postman, Jmeter, SOAP UI, bug tracking tools like Jira, collaboration tools like Trello, Slack, Microsoft Teams and project management tools like Monday or ClickUp and many more… It also requires exceptional communication skills to collaborate effectively with other members of the development team.
An efficient QA engineer demonstrates strong organizational skills, management skills, and a capacity to adapt to shifting priorities. This adaptability enables them to navigate variations in software products and quality assurance processes, balancing the ideal software product and an acceptable result.
Motivating the testing team
Guru99 abstract: teamwork without motivation look like a body without a soul. If you have a motivated team, be sure this QA team will improve your project quality and productivity at times.
Let’s talk…
🤗 Please, share your opinion:
- What career path for Software testing professionals did you choose?
- What testing team roles and responsibilities are in your team?
- What are your QA job title and responsibilities?
Be kind of, spread your experience in a comment we would be glad to hear it! If you have any other duties will free to reach us on Twitter, Reddit, our Telegram channel we will be happy to discuss the above with you.







