Software testing is a mission-critical element of the SDLC where the newly created product undergoes an out-and-out check of its security, performance, usability, and other functional and non-functional aspects. Given the multitude of software quality parameters that need to be validated and the overwhelming number of test cases to be executed, manual testing of the solution will take ages to complete. That is why vetted QA team members can’t do without robust automation tools, which essentially streamline and facilitate the testing process.
But how are you to know that test automation frameworks and platforms did their job well in exposing all bugs, pinpointing potential issues, and indicating problem zones? The only way to discover test outcomes is through test automation reports.
This article will define automated test reporting, unlock its significance and best practices, describe automation test report types, highlight key features that guarantee the effectiveness of testing process, and list the best reporting test automation tools to consider.
What is Test Automation Reporting?
Test reporting comes as the summary phase of text execution, when QA engineers get a test automation report. It is a bottom-line document that contains a rundown of test results in the form of test automation reporting metrics (test coverage, error logs, test pass percentage, test failures, defect density, test stability, and more).
With a testing report at their fingertips, QA teams can improve test management, derive actionable insights into the system’s operation, and understand inadequacies in the development process. Besides, reporting automation mechanisms provide real-time updates on test cases’ performance, allowing for informed decision-making and effective test optimization.
Why Test Automation Matters
When properly drawn and analyzed, testing reports usher in the following perks.
- Visibility. The test automation metrics dashboard serves as the single source of truth for the testing team, whose members can monitor the solution’s functioning in real-time and reveal trends that are instrumental in outlining corrections and adjustments.
- Faster debugging. Testing reports not only highlight every failed test case but also identify its root cause and pinpoint the exact location of the failure, which accelerates defect resolution early in the SDLC.
- Accountability and transparency. Thanks to the straightforward test data presented in the report, all project stakeholders (managers, QA personnel, developers, business owners, etc.) have a clear view of the project’s progress and can assess the product’s overall viability and quality.
- Continuous improvement. Automation reports provide insights regarding the quality of each test suite, helping remove flaky and duplicate tests, enhance test selection and prioritization, focus on high-risk areas, and more.
- Business-level impact. By optimizing resource use and reducing manual effort during test runs, software companies increase the time- and cost-efficiency of the entire development process.
These benefits apply to testing reports of all kinds.
Test Report Types Dissected
Depending on the goal and use cases, test automation reports fall into seven basic categories.
- Summary reports. These provide a general overview of test execution in the form of high-level insights into test outcomes (the number of tests run, passed/failed tests, etc.).
- Detailed execution reports. They offer granular details about specific test cases, such as execution time, pass/fail status, detected errors and issues, and more.
- Trend reports. They resent trends that can be traced in test results over time. Thus, you can monitor progress, pinpoint patterns, and assess improvements or deteriorations in software quality.
- Defect/bug reports. Such documents reflect the bug life cycle and contain a description of the product’s incorrect behaviors in comparison to what the solution should display, as well as indications of the bugs’ severity and priority.
- Coverage reports. By highlighting essential metrics (requirement coverage, code coverage, and multiple specified criteria), they manifest a test’s code and functionality coverage.
- Custom KPIs. The roster of such report parameters can be tailored by testers in accordance with business and technical requirements for the software they are validating.
- AI-prompted reports. Quite understandably, such reports are generated by AI-driven testing tools that rely on generative AI, machine learning, LLMs, and other disruptive technologies.
Regardless of the type of report you use, ensure that the leveraged reporting tool meets the following requirements.
Key Features Ensuring Effective Reporting
The characteristics we will enumerate are non-negotiable qualities for a first-rate automation test reporting solution.
- Accuracy and reliability. All data in reports should be consistent, correct, credible, drawn from reliable sources, validated before finding its way to the document, and contain no false positives or negatives.
- Real-time updates. This capability is pivotal for continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) mechanisms practiced within the DevOps approach to software development, as it enables developers to address problems as soon as they are identified.
- Customizable test automation reporting dashboards. You should have an opportunity to tailor them to suit different audiences and thus showcase metrics (overall and individual test duration and results, list of test cases, environment and build name, etc.) relevant to each stakeholder group.
- Traceability. The report should provide links between test cases and the requirements they verify to ensure each is properly checked, pinpoint any missed functionalities, and manage changes successfully.
- Visualizations. Charts, tables, and graphs enable the presentation of complex data (for instance, pass/fail ratios, defect density, throughput, code coverage, and more) in an easy-to-grasp format and reveal dominant trends within it.
- Notifications. They can be sent via email or as alerts within project management tools and collaboration platforms like Slack. They are vital for setting up CI/CD pipelines, informing stakeholders about test status and results, ensuring proactive issue resolution, and keeping QA team members on the same page.
You can maximize the efficiency of test automation reports by paying attention to the following recommendations.
Best Practices for Meaningful Test Reports
To make the most of testing reports, you should:
- Define goals clearly. You must have a clear vision of who will read the report and why. Depending on the report users, you should standardize the report structure, rely on relevant metrics, ensure the document’s readability, include rich metadata and artifacts, enable shareability and export, leverage collaboration tools, and regularly review and optimize the report.
- Tailor reports to suit a particular audience. Different professionals expect different information from the report. Developers and QA teams require code-level logs and details written in technical language, whereas project managers seek a high-level summary of testing progress and associated risks. Entrepreneurs, on the other hand, look for simple visuals that communicate user satisfaction, business insights, and general project health.
- Don’t just list logs, visualize. You can make results more comprehensible if you involve visual aids (charts, graphs, diagrams, maps, and more) in presenting test outcomes. And remember: it is not only the results that should be visualized. Testing progress can be made more perceptible through visualizations as well.
- Filter/tag tests by feature/module. This move enables testers to group test cases based on the software aspect they validate, thus supporting modular testing and implementing test prioritization, which is crucial for time-constrained scenarios.
- Integrate with bug trackers. Seamless integration of test reports with Azure, Jira, or other bug tracking tools streamlines issue tracking and reporting, enhances bug traceability, improves bug prioritization and management, reduces duplication, and boosts collaboration between developers and testers.
- Monitor trends. Including only the pass/fail rates of tests in the report will allow you to understand what works and what doesn’t, but it won’t get you far in terms of understanding patterns and regularities. You should watch for trends in defect density and severity, test effort, test and code coverage, and other indices to gain knowledgeable insights into the solution’s performance.
You should bear these considerations in mind when choosing a test reporting tool for your project.
Top 10 Testing Automation Reporting Tools: Make your Choice
Here is a list of 10 different platforms that offer robust reporting tools.
1. Testomat.io
By opting for Testomat.io, you will not only acquire a reporting and analytics tool but, in fact, get a comprehensive suite honed for conducting various kinds of tests (unit, integration, acceptance, you name it). The reporting module within the platform provides test outcomes in real-time, grouping them by logical categories and sorting them by execution results, uploads an unlimited number of artifacts in the dedicated cloud storage, attaches screenshots and videos, automates reruns of failed tests, furnishes the entire test results history, visualizes deliverables in the form of heat maps, traces errors in program code, and more.
If you subscribe to the basic Testomat.io version, you will get all these perks free of charge. The two commercial plans (Professional and Enterprise) essentially broaden the roster of core options, offering advanced AI-powered reporting capabilities.
2. TestNG
This solution integrates smoothly with Testomat.io, primarily through the import of automated tests. If you install the ReportNG plugin, you can also enjoy test reporting capabilities either via Testomat or directly in TestNG. The plugin allows for generating visually appealing HTML reports that can be customized through CSS and grouped into categories. Another advantage of TestNG is the ability to present test outcomes in XML in JUnit format, which will stand you in good stead if you leverage CI/CD tools.
3. Allure Report
This open-source tool executes report generation in multiple programming languages and is compatible with all mainstream operating systems (such as Windows, macOS, and Linux). The unquestionable forte of these granular reports is the custom defect classification functionality that helps efficiently detect and categorize bugs and issues. Honed for team collaboration, Allure can be configured with settings manually.
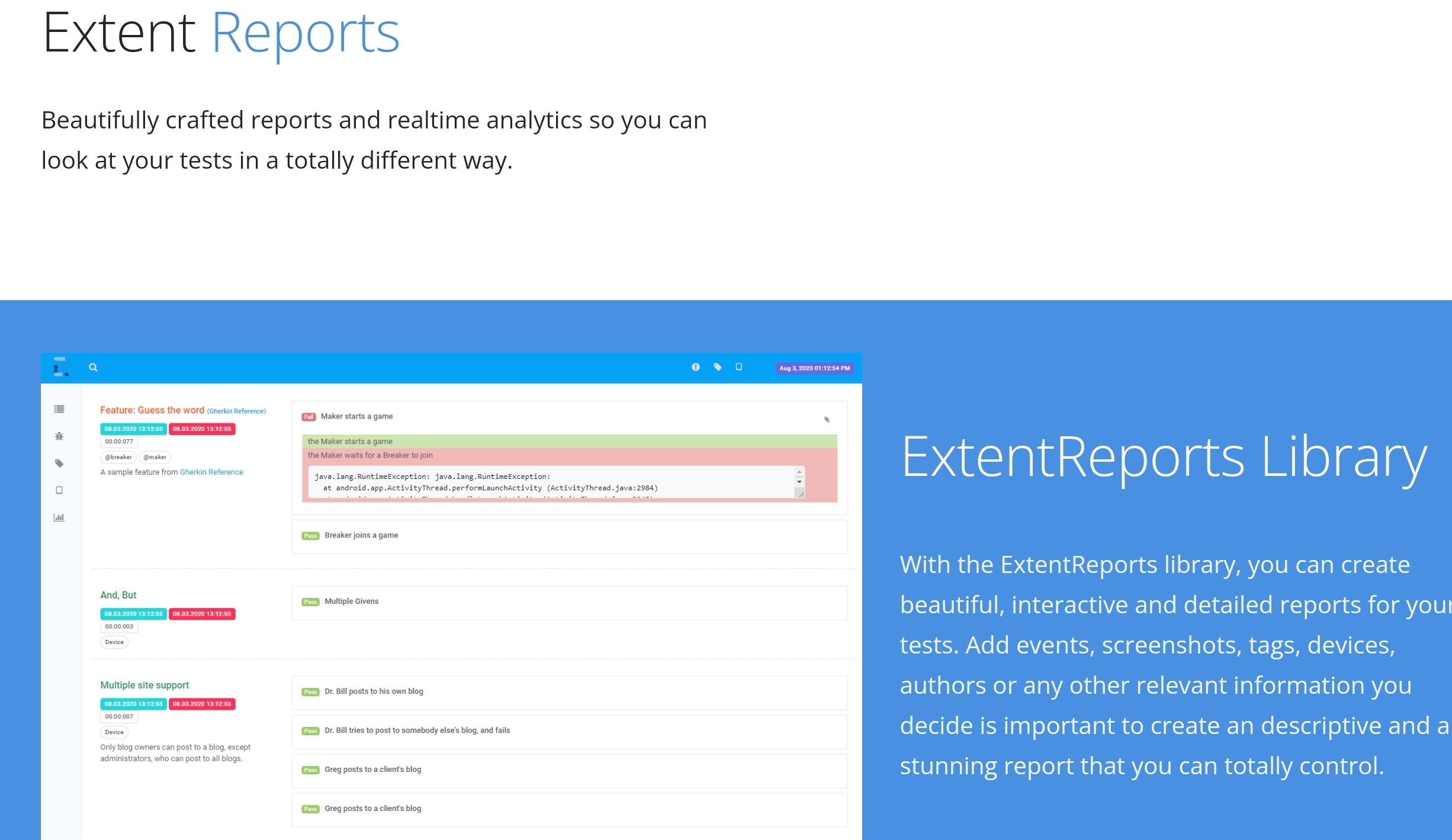
4. ExtentReports
Using its customized features, testers can generate interactive HTML reports that filter test results into categories, allow for screenshot inclusion, and can be viewed in an offline mode from any browser. The solution can be easily integrated with CI/CD tools like Jenkins and various testing frameworks (JUnit, NUnit, and the above-mentioned TestNG).
That said, selecting this open-source library, you should be aware that the project owner has announced its deprecation, with ChainTest being launched as its successor.
5. ReportPortal.io
This web service excels at producing detailed real-time reports, performing efficient defect classification, and maintaining a comprehensive report history. Besides, the resource utilizes AI and ML algorithms to automate test result analysis and plays well with bug tracking tools (for instance, Jira) to make the defect management process a breeze.
6. TestRail
Reports are enabled via TestRail’s test case management platform. Here, you can generate a great range of reports (summary and detailed, project-specific and cross-project, you name it), view the test status, track defects, and even forecast completion. All metrics and statistics are presented on real-time dashboards, while a robust report generation capability enables QA teams to schedule recurring reports and receive email notifications upon completion.
7. X-ray
Acting within the Jira ecosystem, this application is instrumental in tracking test execution progress, test coverage, and defect correlation. The tool’s real-time dashboards are honed for both manual and automated test metrics tracking, while the solution itself easily integrates with Azure DevOps, Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and other CI/CD tools. Also, there are some AI-powered capabilities (like AI-fueled test generation) that enable requirement-driven test design.
8. Jenkins
The platform’s console displays basic information regarding test results, but to generate reports, you need to install the JUnit plugin or any other. It enables the summarizing and visualizing of test outcomes in various formats, which facilitates the analysis of results and contributes to informed decision-making.
9. Katalon TestOps
The platform aggregates data (both historical and real-time) from multiple sources and presents outcomes on customizable dashboards. Thanks to them, you can monitor trends, identify bottlenecks, conduct flaky test analysis, gain insights into platform coverage, and more. Besides, the platform plays well with automation solutions (JUnit, TestNG, Katalon Studio, and others) and CI/CD tools (like Jira or Slack) and provides centralized test orchestration through the scheduling of tests across various environments.
10. Azure DevOps Test Reporting
Azure DevOps has versatile features and tools that streamline and facilitate reporting and analytics. Its test plan features enable the generation of configurable charts, progress reports, and test run summaries that are presented on customized dashboards with the help of pre-built or custom widgets. The analytics service has a built-in pipeline report capability for automatically inferred test results that can be published. Finally, by connecting to Power BI, you can access interactive, advanced test reports.
To Draw a Bottomline
Even if executed with the help of first-rate automation tools, software testing can be an effective step in the QA routine only if it relies on robust reporting procedures. The deliverable of such proceedings is a comprehensive test automation report that improves QA visibility, accelerates debugging, provides accountability and transparency in the validation routine, boosts the quality of test scenarios, and yields significant cost- and time-saving benefits.
Depending on the aspect and granularity of the checked software, test reports can be of different types. Yet, no matter the type, test reports will be more effective if you manage to clearly define report goals, tailor the document for different stakeholders, visualize the results to pinpoint trends, integrate bug trackers, and categorize reports by the software unit they pertain to.
The ultimate success of a test report is largely conditioned by the right choice of an accurate and reliable test reporting tool that supports real-time updates, visualizes results on customizable dashboards, and sends notifications regarding test status and outcomes.