The contemporary healthcare industry is experiencing a tectonic shift. As is the case across other verticals, the healthcare domain is undergoing all-out digitalization. Healthcare professionals are rapidly embracing medical imaging and diagnostic software, clinical decision support systems, telemedicine solutions, mHealth applications, and remote patient monitoring platforms. And we can hardly imagine modern clinics and other healthcare organizations without hospital management systems, EHRs, appointment scheduling solutions, and e-prescribing software.
The reliability and efficiency of healthcare software systems and the medical devices they power are literally a life-and-death issue. If a bug or glitch occurs, it may cost healthcare providers and patients dearly. The former may suffer severe financial and reputational damage, whereas the latter’s health or even life can be endangered. Besides, healthcare data clinics and physicians’ handling should be protected from leakage and unauthorized access. All these challenges to medical software quality and security should be addressed during thorough testing of healthcare software.
This article defines software testing in healthcare, explains the importance of testing healthcare applications, lists the types of healthcare software subject to testing, outlines testing types and challenges of healthcare domain testing management, and recommends testing tools for automated testing of healthcare solutions.
What is Healthcare Software Testing?
Healthcare software development and testing go hand in hand. In fact, testing is an integral part of the SDLC, as healthcare applications developed in previous stages undergo a series of checks. Healthcare software testing is the process designed to guarantee that healthcare systems are ready for use by industry professionals. Very often, it is risk-based testing that directs the QA team’s efforts primarily to software areas where defects are most likely to occur or where the impact of bugs is greatest.
How does testing of software applications in general differ from healthcare testing?
- Goal. The main aim of general testing is to ensure that the software meets functional, usability, and UX requirements. The healthcare software testing process focuses rather on accuracy, reliability, security, and patient safety.
- Compliance. General software testing follows industry standards (mostly ISO), while medical software testing ensures the product complies with stringent legal regulations (HIPAA, GDPR, PIPEDA, etc.).
- Data. Healthcare software systems handle protected health information (PHI), which requires specialized penetration testing techniques; testing other software products boils down to validating the safety of user data, logins, and other information that is not as rigorously protected.
- Integrations. Typically, average software solutions are tested as standalone products with few integrations; healthcare software testing strategies must account for deep interconnections among systems and devices that share data with numerous third parties.
- Required skillset. General testing can be conducted by professionals with standard functional testing expertise. In contrast, a healthcare software testing team must include test engineers with domain-specific knowledge and bring on board numerous stakeholders (doctors, regulators, patients, vendors, pharmacists, and more).
Evidently, software testing in healthcare product development is a mission-critical phase whose importance is conditioned by the specifics of its use cases.
Why Healthcare Software Testing is Crucial
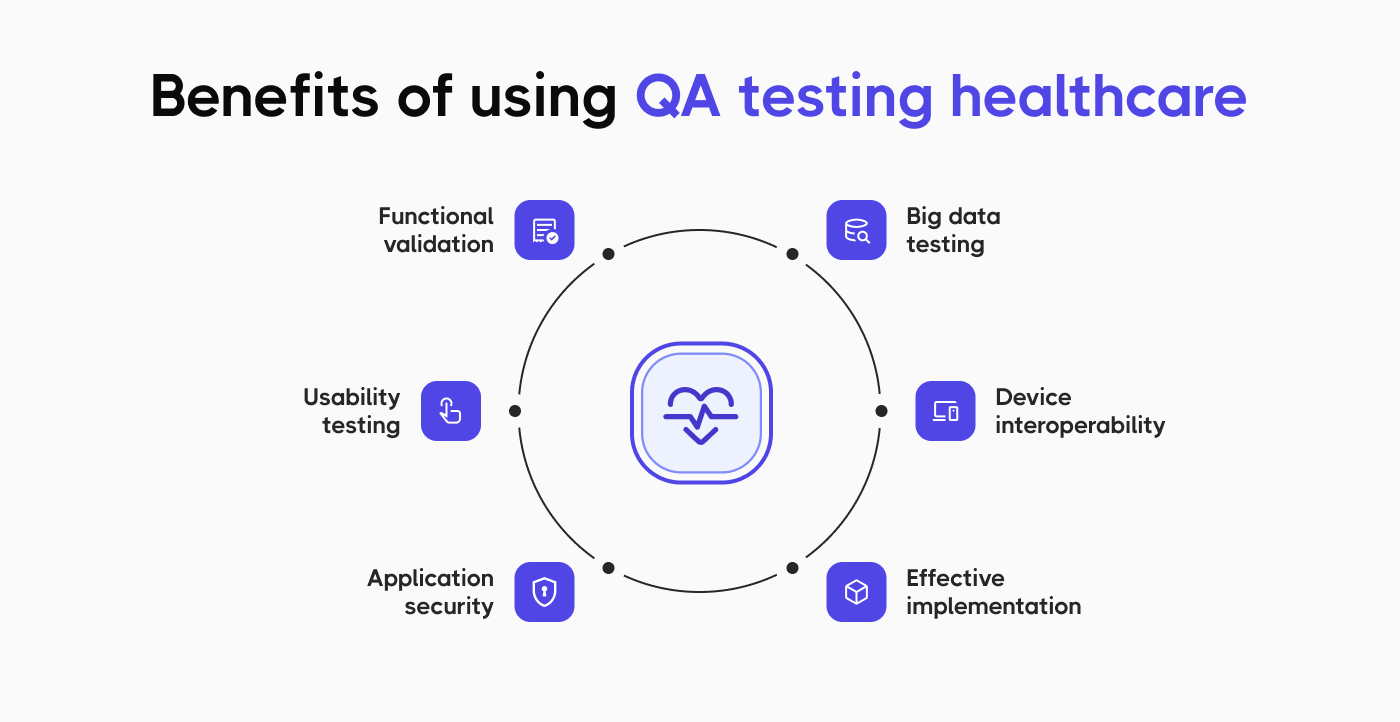
There are several reasons why effective healthcare software testing is vital.
- Patient safety and risk prevention. If medical device software has bugs, they may lead to equipment malfunctions or downtime, wrong diagnoses, incorrect drug doses or prescriptions, and improper treatment, all of which can be fatal.
- Potential data breaches. They result not only in ransomware attacks that stall the regular hospital pipeline and worsen patient outcomes. Stolen data can be used for medical identity theft, fraudulent insurance claims, unauthorized prescriptions, and even medical extortion.
- Legal, reputational, and financial implications of failures. Healthcare software issues lead to substandard services, harming the provider’s reputation and often triggering lawsuits that can result in financial losses.
- Regulatory compliance problems. If compliance testing is inadequate, the healthcare organization will incur severe penalties and fines from law enforcement bodies.
These considerations apply to healthcare software testing projects involving versatile solutions.
Types of Healthcare Software
The most widespread categories of healthcare products include:
Electronic Health/Medical Records (EHR/EMR)
This is an electronic version of a person’s medical history that encompasses diagnoses, lab test results, medications, imaging, and more. Such data is easily shareable and can be updated in real-time. HMR and EMR differ in interoperability and scope. EMR is limited for use within one healthcare organization; EHR can follow the patient across multiple medical providers to be accessed by a broad range of healthcare specialists.
Telemedicine platforms
Such ecosystems comprise specialized software, IoT products, apps, and web portals that enable doctors to provide remote healthcare services via phone, video, or messaging. Telemedicine services include virtual consultations, chronic condition management, prescription refills, follow-up appointments, mental health sessions, and more.
Medical device software
Also known as SaMD (Software as Medical Device), these products act as standalone apps or are embedded in professional hardware (like CT or MRI equipment) to perform monitoring, diagnosing, or treatment. These solutions power wearable devices, process medical images, calculate radiation doses, manage patient data for infusion pumps, exercise clinical decision support, etc.
Healthcare mobile apps
Here belong all kinds of mHealth solutions that patients install on their smartphones and tablets. Such healthcare apps are used for multiple use cases, including fitness tracking, medication reminders, mental wellness counseling, appointment booking, patient portals, and telemedicine services.
Hospital management systems
HMS is a comprehensive, high-quality healthcare software infrastructure (typically cloud-based) honed to streamline and facilitate all workflows within a medical institution. Conventionally, it includes modules such as EHR, patient management, laboratory information systems, administrative and financial tools, operational support solutions, a pharmacy information platform, and more.
All these software products must operate in strict compliance with specific legal norms, which QA teams should incorporate into the models for software healthcare testing they develop.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance in Healthcare Testing
Why is any healthcare software testing strategy and plan hinged on compliance? The industry adheres to a legally mandated framework that safeguards patient safety and data privacy. Non-compliance with healthcare regulations results in hefty fines, criminal charges for executives, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
The core laws regulating healthcare software are:
- HIPAA. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act stipulates how PHI is handled in the USA. It includes the Security Rule, the Privacy Rule, and the Enforcement Rule that regulate data confidentiality.
- GDPR. The General Data Protection Regulation has the same force in the EU as HIPAA in America, defining rules for collecting, storing, and processing personal data.
- FDA regulations. They introduce a risk-based classification system for medical devices and establish requirements for premarket notifications, labeling compliance, facility registration, and postmarket reporting.
- ISO 13485 / IEC 62304. These standards provide guidelines for the development of medical device software. The first establishes the overall framework for quality management systems (including design, risks, suppliers, etc.). The second describes the entire lifecycle of building healthcare software, detailing its development, maintenance, and risk management.
You should know these legal norms inside out when embarking on healthcare app testing.
Major Types of Testing for Healthcare Software
While mapping a comprehensive testing strategy for a healthcare solution, make sure it includes the following procedures.
Functional testing
QA teams leverage this type of testing to ensure the software solution meets all specifications and regulatory norms. They check major shop-floor workflows (billing, scheduling, patient registration, diagnostic reporting, e-prescribing, and more), validating data accuracy and patient safety.
Security testing
Often combined with compliance testing, this process is designed to protect PHI, maintain the system’s inviolability, and ensure regulatory compliance. QA engineers conduct penetration testing, perform vulnerability scanning, validate data encryption, check identity and access management by reviewing authentication and authorization mechanisms, and confirm API security.
Load and performance testing
These testing efforts aim to ensure the solution’s availability and reliability under various conditions and workloads (for example, in peak usage scenarios or emergency situations). The performance test plan usually encompasses load testing, stress testing, endurance (soak) testing, spike testing, and scalability healthcare application testing.
Usability testing
You should validate that the product is easy to navigate and intuitive in usage for various healthcare stakeholders (doctors, nurses, patients, hospital administrative personnel, etc.). Additionally, accessibility considerations are vital for healthcare software, as people with mobility, visual, auditory, and other disabilities should be able to use it.
Integration testing
Since healthcare providers utilize numerous digital products in their workflows, these solutions must play well with one another and with various third-party systems. Integration testing, which goes hand in hand with interoperability testing, ensures seamless and secure data exchange between infrastructure elements, the smooth functioning of APIs, and issue-free communication between medical devices.
All these testing types achieve maximum efficiency when automated.
Test Automation in Healthcare Projects
When we compare manual and automated testing, the second approach has a definite edge in such QA aspects as speed, efficiency, reliability, management of repetitive tasks, early bug detection, and reusability. However, automated testing has its shortcomings too, including high initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs, flakiness and false positives automated tests sometimes contain, improper selection of test cases, and organizational resistance. Moreover, some checks (usability, exploratory, UI/UX, and ad hoc tests) require human judgment and real-time interaction, so manual testing in such cases is the only option.
That said, there are three major benefits that make test automation a go-to approach in most software testing projects.
- Faster regression testing. Automated testing tools can execute hundreds of repetitive test cases quickly by running them across multiple environments. After that, testers receive immediate feedback and can start fixing bugs right off the bat.
- Reduced human error. Machines work tirelessly according to pre-programmed algorithms, minimizing human involvement and the risk of mistakes caused by fatigue or oversight.
- Better test coverage. You can execute large numbers of automated test cases, including complex scenarios and edge cases, in parallel, dramatically accelerating the entire process and shortening time-to-market.
Healthcare software testing services that many providers order from vendors face one more bottleneck: inadequate test management.
Test Management Challenges in Healthcare
Employees tasked with test management in the healthcare domain face several challenges.
- Complex documentation. It’s not only about bulky test plans and strategy, detailed defect and validation reports, or traceability matrices that accompany any QA routine. In healthcare, testers have to deal with huge volumes of patient data and intricate medical scenarios, making paperwork an even tougher row to hoe.
- Traceability between requirements and tests. QA engineers often struggle to maintain bidirectional links in real time that connect tons of shifting requirements, design elements, and risk controls on the one hand and test cases on the other, especially when they use disparate tools (for instance, Excel for testing and Jira for requirements).
- Collaboration between stakeholders. To maximize software testing efficiency, developers, QA teams, and compliance experts should stay on the same page, which can be hard to achieve.
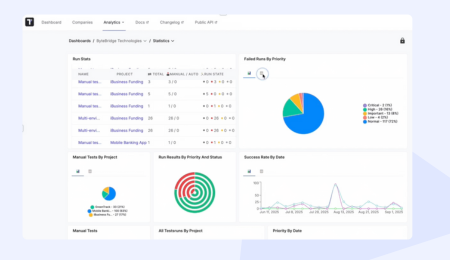
You can accelerate healthcare software testing and improve outcomes by leveraging Testomat.io’s comprehensive automated testing platform.
How Testomat.io Helps Healthcare QA Teams
When you harness Testomat.io’s software testing suite, you are entitled to numerous perks.
Centralized test case management
This is especially valuable for complex projects. An all-in-one tool enables smart test case generation, design, editing, and execution, providing a clear structure for the testing process.
Traceability and documentation
The system links requirements, tests, and results, enabling QA teams to keep the entire picture in view, with documentation serving as a single source of truth and universal reference point.
Integration with automation tools
Thanks to them, you can quickly execute reliable, scalable, and consistent test cases with maximum coverage and minimum resource utilization. Moreover, our automation tools are compatible with CI/CD pipelines, so you can reuse the same test cases each time the code is updated.
Audit-ready test reports
All test reports can be easily exported for viewing by various stakeholders (including regulators), providing a transparent, documented trail that is mission-critical in the heavily regulated healthcare realm.
Key Takeaways
No matter what software solutions a contemporary healthcare provider leverages in its pipeline (EHRs, telemedicine platforms, medical device software, mHealth apps, hospital management systems, you name it), they must be available round-the-clock, accurate, efficient, and safe. All these qualities can be ensured through comprehensive testing that includes functional, security, performance, usability, and integration checks. Additionally, the software should comply with strict data security standards adopted by the industry.
By automating healthcare software testing routines, you can accelerate the process, minimize human error, improve test coverage and reusability, and enhance bug detection. Contact Testomat.io to access a comprehensive testing platform and revolutionize your QA efforts to ensure the security and quality of the healthcare software your organization uses.
Frequently asked questions
What makes healthcare software testing different from general software testing?

Healthcare software testing emphasizes patient safety, data security, and regulatory compliance. Unlike general software, it requires specialized knowledge of HIPAA, GDPR, medical device standards, and integration with multiple systems. Testing ensures medical applications, EHRs, and telemedicine platforms operate accurately, reliably, and safely under real-world healthcare conditions.
Why is automated testing important in healthcare software QA?

Automated testing accelerates regression testing, reduces human error, and ensures broader test coverage for healthcare software. It allows QA teams to quickly validate complex workflows, detect critical bugs, and maintain compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and medical device standards, improving reliability across EHRs, telemedicine apps, and hospital management systems.
Which types of healthcare software require rigorous testing?

All healthcare solutions need thorough QA, including EHR/EMR systems, telemedicine platforms, mHealth apps, medical device software, and hospital management systems. Testing ensures patient safety, accurate diagnostics, secure PHI handling, interoperability, and compliance with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, FDA, and ISO 13485, mitigating risks in medical operations.
What are the main challenges in healthcare software testing?

Healthcare QA teams face complex documentation, strict regulatory requirements, sensitive PHI management, and deep system integrations. Maintaining traceability between requirements and tests, coordinating multiple stakeholders, and handling large volumes of medical data complicate testing. Automated platforms can help streamline workflows and improve accuracy.