Software development teams waste 30-50% of their time setting up test environments instead of actually testing. Meanwhile, 74% of IT projects face delays related to test data quality issues. These statistics point to a problem with measurable costs and a solution with proven returns.
Test data management automates how teams create, mask, subset, and provision data for testing. When implemented effectively, organizations report 400%+ ROI, 25% faster application delivery, and environment refresh times dropping from 3 days to 3 minutes. This article breaks down where these returns come from and how to measure them.
What is test data management and what business impact does it have?
Test data management is the process of provisioning realistic, compliant data to test environments throughout the software development life cycle.
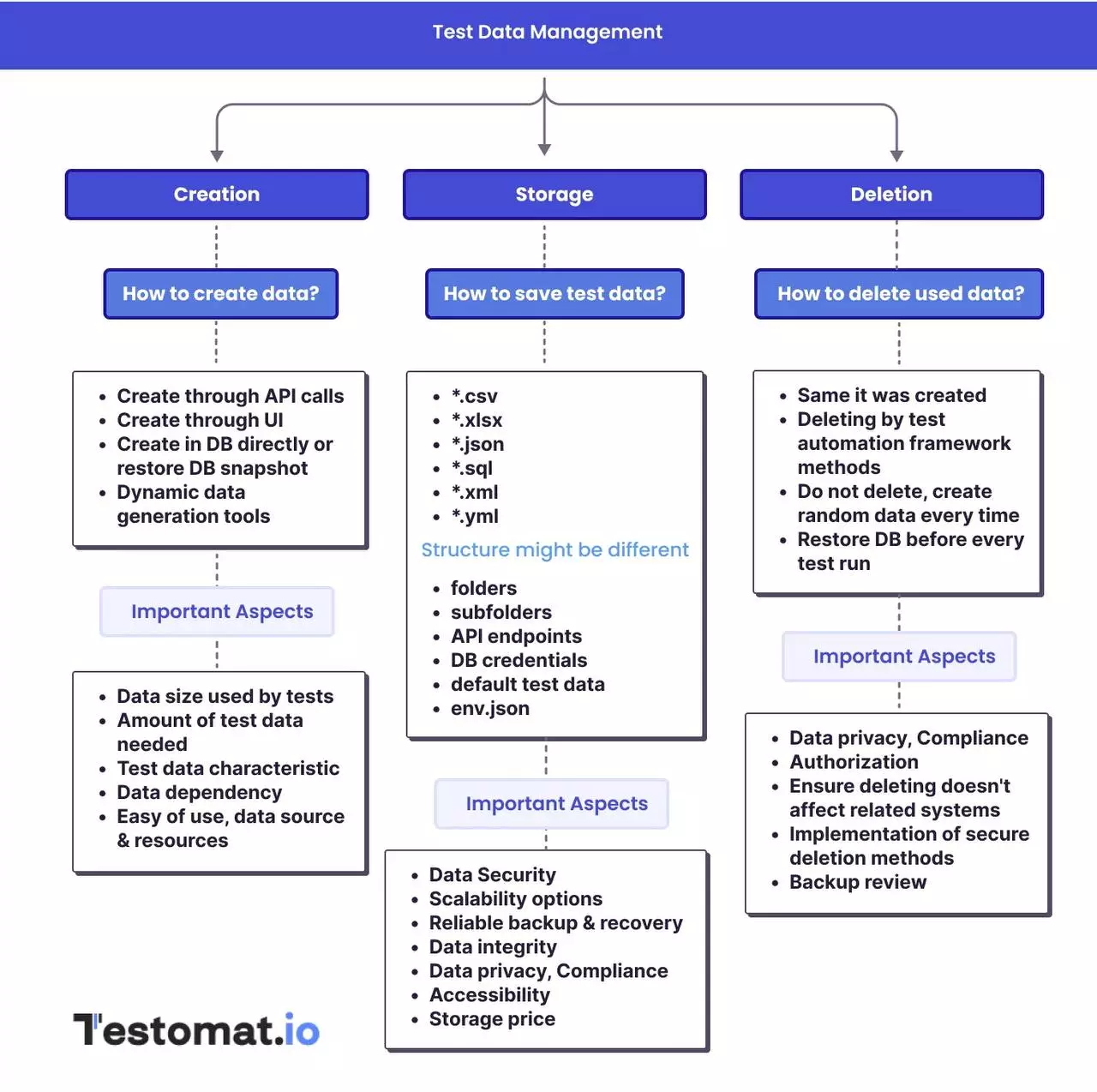
It handles several critical functions:
- Data creation generates test datasets from production sources, synthetic generation, or combinations of both.
- Data masking protects sensitive data by anonymizing personally identifiable information while preserving data relationships.
- Data subsetting reduces dataset size by extracting only relevant records needed for specific test scenarios.
- Test data provisioning delivers this data to test environments quickly and repeatedly.
Without structured test data management, teams manually extract data from production systems, spend days transforming it, and struggle to maintain data privacy compliance. This manual process creates bottlenecks that slow development and testing cycles.
The four dimensions of test data management ROI
Organizations realize return on investment through quantifiable improvements across four areas.
✅ Reduced provisioning costs through automation
Manual test data preparation requires significant labor. Teams spend hours writing scripts to extract data, transform formats, apply masking rules, and load data into test environments. This work is repetitive and error-prone.
Test data management tools automate 40-70% of these manual tasks. A developer who previously spent 8 hours preparing test data can complete the same work in 2-3 hours with automation. At an average developer cost of $60 per hour, this represents $430-516 saved per provisioning cycle.
Multiply this across dozens of test environments refreshed multiple times per sprint, and the labor savings compound quickly. Organizations report reducing test data creation and provisioning costs by 40-70% within the first year.
✅ Faster delivery speeds and time to market
Test data automation directly impacts development velocity. When developers need test data, they access it through self-service portals instead of submitting tickets and waiting days for database administrators to fulfill requests. Real-world examples demonstrate dramatic improvements:
- ITOCHU reduced test environment preparation time from 17 days to 1 hour, achieving a 94% reduction in lead time. This freed their development team to focus on building features instead of managing data infrastructure.
- Trifecta Clinical cut environment provisioning from hours to minutes, enabling 4x more non-production environments without increasing storage costs. This expansion let more developers work in parallel, accelerating their development pipeline.
Organizations implementing test data management report reducing application delivery cycle times by up to 25%. For companies releasing software monthly, this translates to roughly 7 extra days per year available for development or additional releases.
✅ Earlier defect detection through shift-left testing
The cost to fix a defect increases dramatically as it moves through the development pipeline. IBM research shows that fixing a bug during testing costs 15 times more than catching it during design. Defects found during production deployment cost 30-100 times more to correct.
Test data management enables shift-left testing by providing quick access to production-like data early in the development process. Developers can test code against realistic scenarios immediately after writing it, catching issues before they reach QA or production.
This early detection prevents costly late-stage fixes and production incidents. Organizations calculate savings by measuring the reduction in production defects and the associated emergency patches, customer support costs, and reputation damage.
✅ Optimized infrastructure and storage costs
Production databases often contain years of accumulated data spanning gigabytes or terabytes. Replicating full production environments for testing requires substantial storage infrastructure and associated costs.
Test data management techniques address this through intelligent subsetting and synthetic data generation. Subsetting extracts only the data needed for specific test scenarios while maintaining referential integrity. A full production database might be 500GB, but a properly subsetted test environment might need only 50GB to cover relevant test cases.
Organizations report reducing test environment storage by 50-90%. One company cut storage from 12TB to 3.9TB through data virtualization, improving resource efficiency by 600-800%. These savings reduce hardware costs, data center expenses, and cloud storage fees.
Real ROI examples from industry implementations
Financial services organization: $9 million in benefits
A Forrester study analyzed a composite financial services organization implementing test data management tools. Over three years, they realized:
- Total benefits of $9.3 million (present value)
- Total costs of $2.4 million
- Net present value of $6.9 million
- Three-year ROI of 287%
The organization achieved these returns through:
Retail organization: Compliance and speed gains
A large US retailer with $10 billion in annual revenue deployed test data management in 2012 to secure customer data and reduce time-to-market. They achieved:
Significant reduction in time to test and deploy applications while maintaining strict data privacy compliance. Enhanced peace of mind regarding customer personal information security. Comprehensive test coverage through better data availability.
The retailer valued these improvements beyond just cost savings, noting that compliance with data protection regulations and reduced risk of data breaches provided substantial risk mitigation value.
Manufacturing company: 94% lead time reduction
Mattel used test data management to modernize their ERP and WMS systems. Their results included:
- Data refresh times dropped from 5 days to 4-8 hours, cutting cycle time by 85-90%.
- Storage reduction from 12TB to 3.9TB through database virtualization.
- Resource efficiency improvements of 600-800%.
- Lower hardware costs and faster product deployment across sales channels.
These improvements translated to faster innovation cycles and the ability to bring products to market more quickly.
How to calculate ROI for your test data management implementation?
Organizations should quantify expected returns before investing in test data management solutions. The calculation framework includes these components:
- Software licensing: Annual fees for test data management tools, typically priced per user or per environment. Professional plans range from enterprise contracts to per-seat pricing models.
- Implementation costs: Professional services for initial configuration, training, and integration with existing systems. Most implementations require 2-3 months of consulting support.
- Infrastructure: Additional storage or compute resources needed, though these are often offset by savings from data subsetting and virtualization.
- Internal support: FTE costs for ongoing platform administration and support, typically 1-3 full-time employees depending on organization size.
Benefit calculations
Calculate current hours spent on manual test data preparation multiplied by hourly cost of developers and DBAs. Apply the 40-70% automation factor to determine savings.
- Faster delivery: Measure the business value of accelerated release cycles. If faster delivery enables one additional release per year, what revenue or competitive advantage does that generate?
- Reduced production defects: Track production incidents attributed to data-related issues. Calculate the full cost including emergency fixes, customer support, lost revenue, and reputation damage. Apply historical reduction rates to estimate savings.
- Infrastructure optimization: Measure current storage costs for test environments. Apply subsetting ratios (typically 50-90% reduction) to calculate hardware and cloud storage savings.
Sample calculation
A mid-sized company with 50 developers implements test data management.
| Metric | Without TDM | With TDM | Improvement |
| Environment refresh time | 3-5 days | 3-30 minutes | 95-99% reduction |
| Manual provisioning effort | 40-70 hours/month | 10-20 hours/month | 60-70% reduction |
| Test environment storage | 100% of production | 10-30% of production | 70-90% reduction |
| Data masking coverage | 30-50% (manual) | 95-100% (automated) | 2-3x improvement |
| Application delivery cycles | Baseline | 25% faster | 7+ extra days/year |
| Production defects (data-related) | Baseline | 30-50% fewer | Major cost avoidance |
| Developer wait time for data | 2-5 days average | <1 hour average | 95%+ reduction |
| Test data compliance violations | 5-15 per audit | 0-2 per audit | 80-90% reduction |
Costs:
- Software: $150,000 annually
- Implementation: $75,000 one-time
- Infrastructure: $25,000 one-time
- Support: $120,000 annually (2 FTEs)
- Total Year 1: $370,000
- Total Years 2-3: $270,000 annually
Benefits:
- Labor savings: 50 developers × 8 hours/month × $86/hour × 60% automation = $247,680 annually
- Faster delivery: 20% faster releases valued at $500,000 annually
- Reduced defects: 30% fewer production incidents saving $200,000 annually
- Storage savings: $100,000 annually
- Total annual benefits: $1,047,680
Three-year calculation:
- Total benefits: $3,143,040
- Total costs: $910,000
- Net present value: $2,233,040
- ROI: 245%
What are the best test data management practices that maximize ROI?
Manual processes create bottlenecks and consume expensive developer time. Test data automation tools should integrate with CI/CD pipelines to refresh test environments automatically before test runs. This ensures tests always run against current data without human intervention.
Self-service portals let developers and testers request and provision test data without involving DBAs. This reduces wait times from days to minutes while freeing DBAs to focus on production database optimization.
🔎 Read also: How to reduce test failures in CI\CD pipelines?
1️⃣ Implement comprehensive data masking
Data privacy regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA require protecting personally identifiable information in non-production environments. Manual masking is time-consuming and often incomplete, creating compliance risks.
Effective test data management tools automatically discover and classify sensitive data, then apply appropriate masking techniques. This includes:
- Substitution (replacing real names with fake ones)
- Shuffling (redistributing values within a column)
- Encryption (making data unreadable without keys)
- Nulling (removing values entirely for non-critical fields)
- Date variance (shifting dates while preserving relative timing)
Automated masking protects organizations from data breach costs, which average $4.45 million per incident. The cost of implementing proper masking is negligible compared to potential breach penalties and reputation damage.
2️⃣ Use data subsetting to reduce infrastructure costs
Test environments rarely need complete production datasets. A customer service application might need data for 10,000 customers to test all scenarios, not the full 10 million customer records in production.
Intelligent subsetting identifies minimal datasets that provide full test coverage. The key is maintaining referential integrity, if you subset customer records, you must include their related orders, invoices, and support tickets.
Organizations report reducing test environment storage by 70-90% through subsetting. This cuts cloud storage costs, reduces backup times, and improves test execution speed since tests work with smaller datasets.
3️⃣ Generate synthetic data for edge cases
Production data represents typical use cases but often lacks edge cases needed for thorough testing. Synthetic data generation creates artificial records for scenarios like:
- Maximum field lengths and boundary values
- Unusual character sets and international formats
- High-volume stress testing scenarios
- New features not yet used in production
Synthetic data also eliminates data privacy concerns since it contains no real customer information. Teams can share synthetic datasets freely across development, QA, and third-party contractors without compliance risks.
4️⃣ Centralize test data management across teams
Fragmented test data approaches create inefficiencies. Different teams maintain separate processes for extracting and masking data, leading to duplicated effort and inconsistent data quality.
A centralized test data management platform provides:
- Single source for provisioning test data to all environments
- Consistent masking rules applied organization-wide
- Data versioning and rollback capabilities
- Usage metrics showing which teams consume most resources
- Cost allocation for chargeback to business units
Centralization improves visibility into test data consumption patterns and helps optimize resource allocation.
5️⃣ Integrate with test management tools
Test data management should connect directly to test execution platforms. When test automation frameworks like Testomat.io execute test cases, they should automatically provision required test data, run tests, then clean up data after completion. This integration ensures:
- Tests always have required data available
- Test results are reproducible since data state is consistent
- Failed tests can be debugged with the exact data that caused failures
- Test coverage metrics account for data variety across test runs
What are the common challenges in test data management and their ROI impact?
Managing sensitive data across development and testing teams creates significant compliance risks. Organizations face hefty fines for GDPR violations (up to 4% of global revenue) or HIPAA breaches (up to $1.5 million per violation).
The challenge is discovering all sensitive data across complex data sources, applying appropriate protection, and maintaining audit trails proving compliance.
ROI impact: Proper data masking and anonymization prevent breach costs and regulatory fines. Organizations calculate this benefit by estimating the probability-adjusted cost of potential violations, typically $500,000-5 million depending on industry and data volumes.
Maintaining referential integrity
Production databases have complex relationships between tables. Customer records link to orders, which link to products, which link to inventory. Subsetting customer data without related records creates useless test datasets.
Manual approaches to maintaining referential integrity are tedious and error-prone. Test data management tools use metadata analysis to identify relationships and automatically include dependent records.
ROI impact: Tests using data without referential integrity produce false failures, wasting tester time investigating non-issues. Organizations report 10-20% reduction in test debugging time when referential integrity is maintained automatically.
Keeping test data fresh and relevant
Stale test data causes false positives in testing. If production schema changes but test environments use outdated data structures, tests fail for wrong reasons. Teams waste time troubleshooting issues that don’t exist in production.
The traditional approach of quarterly or monthly refreshes means test data is often weeks out of sync with production. Modern test data provisioning enables daily or on-demand refreshes.
ROI impact: Stale data reduces test reliability and effectiveness. Organizations estimate 15-25% of test failures are attributable to data quality issues rather than actual code defects. Faster refresh cycles reduce this waste.
Scaling test data across growing teams
As development teams grow and adopt agile methodologies, demand for test environments increases. Traditional approaches can’t scale to provision dozens of environments daily without massive infrastructure investments.
Data virtualization addresses this by storing one masked production copy and creating virtual instances for each test environment. These virtual environments share underlying storage while appearing as independent databases to applications.
ROI impact: Organizations report supporting 4-10x more test environments using the same physical infrastructure through virtualization. This enables parallel development and testing without proportional infrastructure costs.
Test data management tools and platform selection
Several factors determine which test data management solution delivers best ROI for specific organizations.
- Data discovery and profiling: Automatically scan data sources to identify sensitive fields and data relationships. This reduces manual effort in cataloging data and ensures nothing is missed during masking.
- Multiple masking techniques: Support various anonymization methods suitable for different data types and compliance requirements. Financial data needs different treatment than healthcare data.
- Synthetic data generation: Create artificial test data for scenarios not represented in production or when production data cannot be used due to privacy constraints.
- Data subsetting with referential integrity: Extract minimal datasets while maintaining database relationships automatically rather than through manual scripting.
- Version control and rollback: Track data changes and restore previous states when tests need to be rerun against specific data versions.
- Self-service provisioning: Let developers and testers request and provision data through portals without involving DBAs for every request.
- CI/CD integration: Connect to build pipelines for automated test data refresh triggered by code commits or scheduled builds.
- Multi-source support: Handle data from various databases (Oracle, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL), file formats (CSV, JSON, XML), and cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP).
Integration with test management tools
Test data management works best when integrated with comprehensive test management platforms. When test automation executes, it needs appropriate data available in test environments. The test management system coordinates this by:
Triggering test data provisioning before test runs begin. Selecting appropriate data subsets matching test case requirements. Recording which data version was used for each test execution. Providing data cleanup after test completion.
Platforms like Testomat.io support this integration through APIs and CI/CD connectors. This creates seamless workflows where test execution automatically includes proper data preparation.
How to measure ongoing ROI and optimization?
After implementing test data management, organizations should track metrics proving continued value delivery.
| Metric Category | Metric | Description | Target / Expected Outcome |
| Operational Metrics | Data provisioning time | Average time taken to fulfill a test data request from submission to delivery | Reduction from days to minutes or hours |
| Storage utilization | Total storage consumed by test environments over time | 50–80% reduction through data subsetting and virtualization | |
| Environment refresh frequency | Frequency at which test data environments are refreshed or updated | Shift from monthly/quarterly to weekly or on-demand | |
| Self-service adoption | Percentage of test data requests fulfilled via self-service portals | 80%+ requests handled without DBA involvement | |
| Quality Metrics | Test failure analysis | Percentage of test failures caused by data quality issues versus code defects | <5% of failures attributable to test data issues |
| Production defect reduction | Number of production incidents related to data handling or data defects | 30–50% reduction in data-related production issues | |
| Test data coverage | Degree to which test scenarios (including edge cases) are supported by available test data | Comprehensive coverage using masked, subset, and synthetic data | |
| Business Metrics | Release velocity | Deployment frequency and lead time from code commit to production | Measurable increase in release frequency and faster lead times |
| Developer productivity | Time spent waiting for test data compared to active development time | 40–60% reduction in test data wait time | |
| Compliance audit results | Audit findings related to data privacy and security in test environments | Zero major compliance findings | |
| Cost per test environment | Total cost divided by number of test environments supported | Continuous reduction as virtualization and reuse scale |
Key takeaways for maximizing test data management ROI
The ROI of test data management comes from automating repetitive manual work, reducing infrastructure costs, accelerating delivery, and preventing costly production defects.
Organizations implementing test data management solutions report 400%+ ROI within 3 years through measurable improvements in provisioning efficiency, delivery speed, and software quality.
The investment pays for itself within 6-12 months through labor savings alone, with compounding benefits as teams optimize workflows and scale adoption across the organization.
Frequently asked questions
How quickly can we see ROI from test data management implementation?

Organizations typically see initial returns within 3-6 months as automation reduces manual data provisioning work. Full ROI realization takes 12-18 months once all teams adopt the platform and optimize workflows. Labor savings appear immediately while infrastructure optimization happens gradually as teams subset data and adopt virtualization.
What ROI can smaller development teams expect compared to enterprises?

Smaller teams still realize 200-300% ROI through automation and faster delivery, though absolute dollar savings are lower. A 10-person team saving 5 hours per developer weekly at $80/hour saves $208,000 annually. Enterprise teams with 500+ developers see proportionally larger savings but percentage ROI is comparable across organization sizes.
What ongoing costs impact long-term ROI calculations?

Annual software licensing, platform support staff (typically 1-3 FTEs), and incremental infrastructure costs. However, these costs remain relatively flat while benefits compound as more teams adopt the platform and processes mature. Year-three ROI is typically 30-50% higher than year-one ROI as utilization increases and teams discover additional optimization opportunities.