The software testing industry has witnessed more transformation in the past few years than in the previous decade combined. Remember when “automation” meant recording macros in Excel and teams debated whether Selenium was worth the learning curve? Those days feel like ancient history now that AI-driven testing tools can generate comprehensive test scenarios faster than most QA teams can finish their morning standup.
The software testing trends in 2026 aren’t just incremental improvements, they’re fundamental shifts in how teams approach quality assurance. And unlike previous “revolutionary” trends that turned out to be rebranded buzzwords, these changes are backed by real tools, proven methodologies, and tangible results that even the most skeptical QA veterans can’t ignore.
This comprehensive guide explores the top software testing trends shaping software testing in 2026, written from the perspective of someone who understands the real challenges of implementing these practices. Because reading about trends is easy, implementing them while maintaining sanity, meeting deadlines, and not breaking production? That’s the real challenge.
The State of Software Testing in 2026: How Far We’ve Come
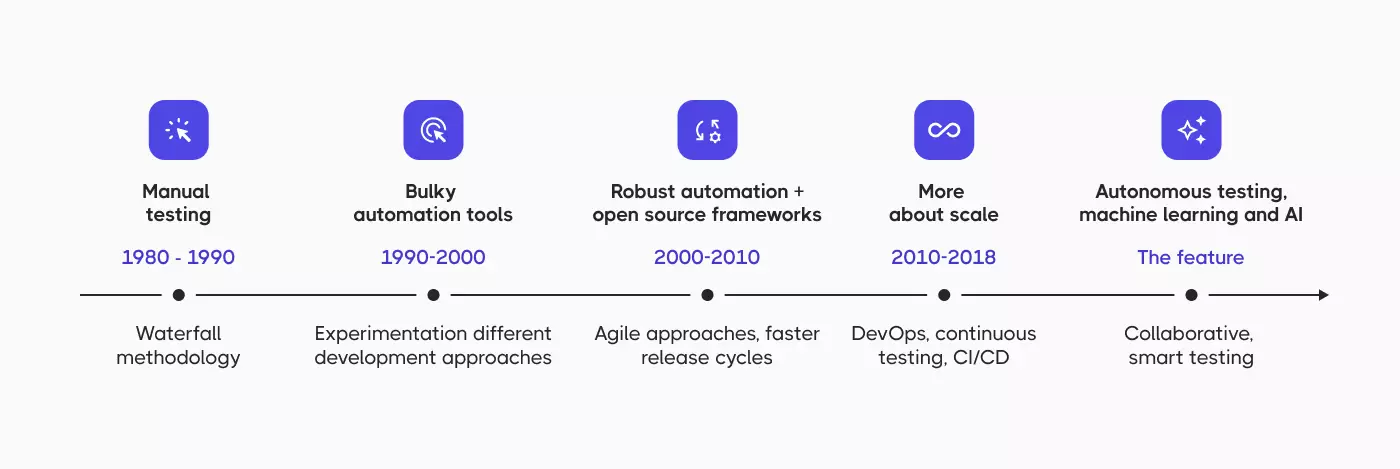
The current testing landscape bears little resemblance to traditional testing approaches where manual testing dominated and automation testing was considered “nice to have.” Testing has become integrated throughout the software development lifecycle, not just tacked on at the end when everyone’s already exhausted and the deadline was yesterday.
Modern software applications demand testing across web, mobile, API, IoT, and platforms that didn’t exist five years ago. Security testing runs continuously because data breaches are expensive. Performance testing happens in production because test environments never quite replicate real-world chaos. Accessibility testing is mandatory because lawsuits are even more expensive than breaches.
The testing process has evolved from “does it work?” to “does it work quickly, securely, accessibly, and reliably under conditions we haven’t even thought of yet?” Testing ensures not just functional correctness but performance, security, usability, and compliance across an ever-expanding matrix of scenarios.
Key shifts in the testing landscape:
- Testing without early involvement means catching expensive problems late
- Testing has become continuous rather than a final phase
- Testing across multiple platforms simultaneously is now standard
- Testing must address security, performance, and accessibility from day one
- Testing activities integrate with DevOps and CI/CD workflows
- Testing tools have evolved from simple recorders to AI-powered platforms
Anyone claiming their QA process looks the same as it did three years ago either works on legacy systems or isn’t being entirely honest. The emerging trends in software testing force adaptation whether teams are ready or not, though being ready certainly helps.
Top Software Testing Trends for 2026
Let’s explore the latest trends in software testing that are transforming how QA teams work, deliver high-quality software, and ensure software meets increasingly demanding requirements.
1. AI and Machine Learning: The Game-Changer in Testing
AI in software testing has moved from “interesting research project” to “how did we ever live without this?” faster than most emerging software testing trends. The use of AI isn’t replacing QA teams (despite what some vendors’ marketing materials might imply), it’s handling the tedious stuff that was slowly driving everyone insane.
How AI Testing Transforms the QA Process
Early attempts at AI testing produced test cases that looked like they were written by someone who’d never actually used software. Current AI and machine learning tools analyze application behavior, historical test data, and user patterns to generate genuinely useful test scenarios. They identify edge cases human testers might miss, not because humans are bad at their jobs, but because humans can’t simultaneously consider 47 different variable combinations while also remembering to eat lunch.
AI-powered test generation creates:
- Comprehensive test cases from requirements and user stories
- Intelligent test data that covers diverse scenarios and edge cases
- Test scenarios based on production usage patterns
- Gap analysis identifying missing test coverage
- Prioritized test suites focusing on high-risk areas
The good AI testing tools integrate seamlessly with testing platforms like Testomat.io’s Enterprise plan, which includes AI agents that assist with test creation without requiring a PhD in machine learning.
Self-Healing Test Scripts
The maintenance burden of automated tests has been the dirty secret of test automation for years. Write 500 test scripts, enjoy six months of stability, then spend the next year fixing broken tests because the dev team changed a CSS class name. AI and ML algorithms now detect when application changes break tests and automatically update test scripts or suggest fixes.
Self-healing capabilities include:
- Automatic locator updates when UI elements change
- Smart wait strategies that adapt to application behavior
- Alternative element identification when primary selectors fail
- Pattern recognition for similar test failures
- Suggested fixes with confidence scores
This self-healing capability doesn’t eliminate maintenance entirely, nothing’s that magical, but it significantly reduces the “why is everything broken again?” Monday morning panic.
Predictive Analytics for Defects
AI analyzes patterns across test results, code commits, and production incidents to predict where bugs are most likely to lurk. This predictive capability helps QA teams focus testing efforts on high-risk areas rather than wasting time testing stable components that haven’t changed in months.
Predictive analytics provide:
- Risk scores for code changes based on historical data
- Defect probability by module, feature, or component
- Optimal test execution strategies based on change impact
- Resource allocation recommendations
- Correlation between code complexity and defect rates
Intelligent Test Data Generation
Creating realistic test data that respects privacy regulations, maintains referential integrity, and covers edge cases is surprisingly difficult. AI-powered tools generate synthetic test data that looks realistic without containing actual customer information.
AI understands context:
- Payment testing receives realistic transaction patterns
- Healthcare applications get compliant medical records
- E-commerce platforms receive sensible shopping behaviors
- Financial systems get appropriate account hierarchies
- Social platforms generate realistic user interaction patterns
The latest trends in software testing show AI integration becoming standard rather than experimental. Teams that embrace AI-driven testing gain significant productivity improvements while those who don’t spend their time on busywork that robots could handle.
2. Shift-Left and Shift-Right Testing: Testing Everywhere
The shift-left testing movement told everyone to test earlier. Now shift-right testing says test in production too. But despite the terminology proliferation, shift-left and shift-right testing represent genuinely valuable approaches when implemented thoughtfully.
Shift-left testing moves testing activities earlier in the software development process, which sounds obvious until remembering how many organizations still treat testing as something that happens after development is “done.”
Core shift-left testing practices:
- Test case creation begins during requirements analysis
- API testing starts before UI development
- Security testing integrates into code reviews
- Accessibility testing informs design decisions
- Unit tests written alongside production code
- BDD scenarios created collaboratively with stakeholders
Modern shift-left testing starts at requirements with test case creation from user stories. This early testing approach catches defects when they’re cheapest to fix, before they cascade through the system like that time someone accidentally deleted the production database (hypothetically speaking, of course).
Behavior-driven development (BDD) enables shift-left testing by creating executable specifications that serve as both documentation and automated tests. Testomat.io’s Gherkin editor with auto-completion lets non-technical stakeholders write test scenarios in plain language, ensuring comprehensive coverage from multiple perspectives.
3. Continuous Testing in CI/CD: Testing Never Stops
Continuous testing has evolved from aspirational buzzword to mandatory infrastructure in modern software development. Testing is no longer a phase that happens between coding and deployment, it’s an ongoing activity that executes automatically throughout CI/CD pipelines, providing immediate feedback on every code change.
Automated Pipeline Integration
In 2026, every code commit triggers comprehensive automated tests spanning multiple test types:
Test execution hierarchy in CI/CD:
- Immediate (on commit): Unit tests, static code analysis, security scans
- Fast feedback (5-10 min): API testing, smoke tests, critical path validation
- Standard (15-30 min): Integration tests, functional testing, database tests
- Extended (30-60 min): End-to-end testing, cross-browser tests, performance testing
- Scheduled: Comprehensive regression testing, long-running performance tests, exploratory testing
These testing tasks execute in parallel because waiting for sequential test execution is how teams ensure they never deploy anything. Results appear within minutes instead of hours, providing fast feedback that actually influences development decisions rather than confirming what everyone already suspected.
4. Test Automation Expansion: Beyond Web UI Testing
Test automation continues evolving beyond “automate the happy path on the web UI” to cover increasingly complex testing scenarios and application types that didn’t exist when Selenium was the only game in town.
As microservices architectures proliferate, API testing has become more critical than UI testing for many applications. Testing ensures APIs maintain their contracts, handle errors gracefully, perform within acceptable latency bounds, and secure data appropriately.
Why API testing dominates modern testing strategies:
- Faster execution than UI tests (seconds vs. minutes)
- Better business logic coverage without UI dependencies
- Earlier testing in the software development process
- More stable than UI tests (no layout changes breaking tests)
- Easier to implement data-driven testing
- Superior for microservices validation
Automated API tests execute faster than UI tests, provide better coverage of business logic, and don’t break every time the design team decides buttons should be rounded instead of square. They’re the unsung heroes of modern testing strategies.
5. Security Testing Integration: Security as a Continuous Priority
Security testing and cybersecurity testing are no longer optional activities relegated to pre-release security audits. In 2026, security testing integrates throughout the software development process as standard practice, driven by increasing regulatory requirements and the realization that data breaches are career-limiting events.
Shift-Left Security
Security testing begins at the code level with static analysis tools scanning for vulnerabilities during development. Dynamic security testing runs continuously in CI/CD pipelines, checking for common vulnerabilities.
Key security testing activities throughout the software development lifecycle:
- Design phase: Threat modeling, security architecture review
- Development: Static application security testing (SAST), secure code review
- Build: Dependency vulnerability scanning, license compliance
- Testing: Dynamic application security testing (DAST), penetration testing
- Deployment: Container security scanning, infrastructure validation
- Production: Runtime application self-protection (RASP), security monitoring
Compliance Automation
Regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, and industry-specific standards demand demonstrable security controls. Automated compliance testing validates that applications meet these requirements while generating audit trails and evidence of security testing activities.
Common compliance testing requirements:
- Data encryption in transit and at rest
- Access control and authentication strength
- Audit logging and monitoring
- Data retention and deletion policies
- Privacy controls and consent management
- Incident response capabilities
Modern testing platforms support security testing integration by providing secure test data management, audit logs of testing activities, and role-based access controls. Testomat.io’s Enterprise plan includes system usage audits and role-based access controls that help organizations maintain security throughout the testing process.
6. Advanced Test Data Management with AI
Test data management has historically been the unglamorous, tedious aspect of software testing that everyone knows matters but nobody wants to handle. AI and machine learning are transforming this landscape in 2026, making test data generation almost enjoyable. Almost.
Synthetic Data Generation
AI algorithms analyze production data patterns and generate synthetic test data that maintains statistical properties and relationships without containing actual customer information. This synthetic data enables realistic testing while ensuring privacy compliance.
Benefits of AI-powered test data generation:
- Privacy compliance without manual data masking
- Unlimited data volume without storage constraints
- Domain-appropriate data for realistic testing
- Edge case coverage including rare scenarios
- Referential integrity maintenance across related data
- Dynamic generation for each test run
| Aspect | Traditional Approach | AI-Powered Approach |
| Data Source | Production copies with masking | Synthetically generated from patterns |
| Privacy Risk | Medium to high (masking failures) | Minimal (no real customer data) |
| Setup Time | Hours to days | Minutes |
| Data Variety | Limited to production patterns | Unlimited including edge cases |
| Maintenance | Manual updates required | Automatic adaptation to schema changes |
| Compliance | Requires extensive validation | Built-in compliance by design |
| Storage Costs | High (large database copies) | Low (generated on-demand) |
7. Cloud-Based Testing Platforms: Scalability and Collaboration
Cloud-based testing has matured from emerging trend to standard infrastructure in 2026. Testing platforms leverage cloud capabilities to provide unprecedented scalability, accessibility, and collaboration features.
Elastic Testing Infrastructure
Cloud-based testing enables teams to scale testing infrastructure dynamically based on demand. Need to run 10,000 parallel tests before a major release? Provision resources for three hours, run tests, release resources. This elasticity eliminates the traditional choice between over-provisioning infrastructure (expensive and wasteful) or under-provisioning (creates bottlenecks when testing needs spike).
Cloud testing advantages:
- Dynamic resource scaling based on demand
- Global accessibility for distributed teams
- No physical infrastructure maintenance
- Automatic updates and feature additions
- Built-in disaster recovery and redundancy
- Pay-per-use cost optimization
Cross-Browser and Device Testing
Cloud platforms maintain extensive browser and device farms for testing software across diverse user environments. Instead of maintaining local device labs that look like electronics recycling centers, teams access thousands of browser-device-OS combinations through cloud services.
Coverage provided by cloud testing platforms:
- Desktop browsers: Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge (current and legacy versions)
- Mobile devices: iOS and Android across multiple versions
- Operating systems: Windows, macOS, Linux distributions
- Screen resolutions and viewport sizes
- Real device testing vs. emulators/simulators
- Network condition simulation (3G, 4G, 5G, WiFi)
8. Accessibility Testing: Inclusive Design as Standard Practice
Accessibility testing has moved from “nice-to-have” checkbox to essential requirement in 2026, driven by legal mandates, ethical considerations, and recognition that accessible design benefits everyone.
Automated accessibility testing covers:
- WCAG 2.1/2.2 compliance validation
- ARIA attribute correctness
- Keyboard navigation completeness
- Color contrast ratios
- Semantic HTML structure
- Form label associations
- Focus management
- Screen reader compatibility
Modern testing tools include automated accessibility testing that integrates into CI/CD pipelines, catching accessibility issues before they reach production and before lawsuits arrive.
Rather than treating accessibility as a final checkpoint, modern development practices incorporate accessibility considerations from design through implementation:
Accessibility integration points:
- Design: Color contrast checking, focus indicator design, touch target sizing
- Development: Semantic HTML, ARIA implementation, keyboard support
- Component testing: Individual component accessibility validation
- Integration testing: Complete flow accessibility verification
- End-to-end testing: Full user journey accessibility confirmation
Including accessibility testing in comprehensive test strategies ensures software reaches the widest possible audience and meets legal requirements across jurisdictions.
9. Performance Testing Evolution: Continuous Performance Validation
Performance testing in 2026 extends beyond pre-release load testing to encompass continuous performance monitoring and optimization throughout the software development lifecycle and in production.
| Testing Type | Purpose | When to Run | Key Metrics |
| Load Testing | Validate performance under expected load | Before releases, after significant changes | Response time, throughput, error rates |
| Stress Testing | Determine breaking points | Before capacity planning, annually | Maximum concurrent users, resource limits |
| Spike Testing | Validate sudden traffic increases | Before marketing campaigns, seasonal events | Recovery time, error handling, auto-scaling |
| Endurance Testing | Identify memory leaks and degradation | Before releases, quarterly | Memory usage over time, response time trends |
| Scalability Testing | Validate horizontal/vertical scaling | Architecture changes, capacity planning | Linear scaling metrics, cost per user |
10. Exploratory Testing: The Human Element Remains Essential
Despite advances in test automation and AI-driven testing, exploratory testing maintains its crucial role in comprehensive testing strategies. Human creativity, intuition, and contextual understanding continue providing value that automation cannot replicate.
Modern exploratory testing is more structured than “click around and see what breaks”:
- Charter: Defines testing scope, objectives, and focus areas
- Time box: Typically 60-90 minutes for focused testing
- Testing notes: Real-time documentation of activities and observations
- Issues found: Defects, usability problems, and improvement suggestions
- Debrief: Team discussion of findings and insights
- Follow-up: Converting discoveries to automated tests
How Testomat.io Addresses Modern Testing Trends
Testomat.io positions itself at the intersection of these software testing trends, providing a comprehensive platform that helps teams implement modern testing practices effectively.
Key Capabilities Addressing 2026 Trends
AI-Powered Testing:

- AI test generation from requirements
- AI agents for test management assistance
- AI requirements management and coverage tracking
- Intelligent test suggestions and improvements
Continuous Testing Support:
- Native CI/CD integrations (Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Azure DevOps)
- Built-in reporters for popular frameworks
- Real-time test execution tracking
- Parallel execution support
Unified Test Management:
- Single platform for manual and automated tests
- Support for UI, API, mobile, and specialized testing
- Centralized test case repository
- Cross-project visibility (Enterprise)
Collaboration Features:
- Gherkin editor with auto-completion for BDD
- Comments and discussions on test cases
- Assignments with email notifications
- Role-based access controls (Enterprise)
- Real-time team collaboration
Comprehensive Analytics:

- Real-time dashboards
- Flaky test detection
- Automation coverage metrics
- Slowest test analysis
- Requirements coverage tracking
- Custom charts and timelines
Enterprise Scalability:
- Support for up to 100,000 tests per project
- Unlimited artifacts storage via S3
- Parallel execution capabilities
- Self-hosted deployment option
Integration Ecosystem:
- Bidirectional Jira synchronization
- GitHub and Azure DevOps integration
- Slack and Microsoft Teams notifications
- Cucumber and BDD framework support
- S3-compatible artifact storage
Implementing These Trends: Practical Action Plan
Understanding software testing trends in 2026 is valuable, implementing them while maintaining sanity, meeting deadlines, and not breaking production requires strategy.
Phase 1: Assessment (Weeks 1-2)
Evaluate current state:
- Document existing testing processes and tools
- Identify test coverage gaps and pain points
- Assess team skills and knowledge gaps
- Review test automation maturity level
- Analyze defect patterns and escape rates
- Benchmark current testing metrics
Prioritize improvements:
- Rank trends by potential impact for your context
- Consider quick wins vs. long-term transformations
- Align with business goals and software delivery objectives
- Evaluate resource requirements and constraints
Phase 2: Quick Wins (Weeks 3-8)
Implement high-impact, low-effort improvements:
- Set up basic continuous testing for critical paths
- Integrate existing tests with CI/CD pipelines
- Implement test reporting dashboards
- Establish performance budgets for key metrics
- Add accessibility testing to critical flows
- Improve test data management for problematic areas
Phase 3: Strategic Initiatives (Months 3-6)
Implement transformational changes:
- Adopt AI-powered test generation for new features
- Establish comprehensive shift-left testing practices
- Implement security testing throughout lifecycle
- Expand API testing coverage
- Deploy cloud-based testing infrastructure
- Create BDD scenarios with stakeholder involvement
Phase 4: Continuous Improvement (Ongoing)
Sustain and optimize:
- Monitor testing metrics and trends
- Refine testing strategies based on data
- Invest in ongoing team training
- Evaluate and adopt new testing tools
- Share knowledge across teams
- Celebrate wins and learn from failures
Skills Development Roadmap
Essential skills for modern QA teams:
- AI-driven testing tools and methodologies
- API testing frameworks and best practices
- Security testing fundamentals and OWASP Top 10
- Performance testing and analysis
- Cloud platform familiarity (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- CI/CD pipeline configuration and optimization
- Test automation frameworks (Selenium, Playwright, Cypress)
- Programming fundamentals (JavaScript, Python, Java)
- BDD and Gherkin syntax
- Accessibility standards (WCAG 2.1/2.2)
The Future of Software Testing: What’s Coming Next
Looking beyond 2026, several emerging software testing trends suggest how the testing landscape will continue evolving.
Autonomous Testing Systems
AI and machine learning will progress toward truly autonomous testing where systems not only generate and maintain tests but also determine what needs testing based on code changes, usage patterns, and risk analysis. These systems will continuously optimize test suites, removing redundant tests and adding coverage for new scenarios without human intervention.
Quantum Computing Impact
As quantum computing becomes more accessible, it will enable testing scenarios currently impractical with classical computing, particularly for cryptographic validation and complex system simulations. Testing software may need new methodologies to validate quantum algorithms and quantum-resistant security implementations.
Extended Reality Testing
As augmented reality and virtual reality applications proliferate beyond gaming, specialized testing methods for XR will mature. Testing these immersive experiences requires validating spatial interactions, motion tracking, multi-sensory feedback, and comfort factors.
Ethical AI Testing
As AI systems make increasingly important decisions, testing must validate not just technical correctness but ethical behavior. Testing ensures AI systems don’t exhibit bias, respect privacy, operate transparently, and fail safely.
Environmental Impact Testing
Software’s environmental footprint becomes a testing concern as organizations commit to sustainability goals. Testing will include energy consumption metrics, carbon footprint analysis, and optimization for environmental efficiency.
Conclusion: Embrace the Evolution of Software Testing
The software testing trends for 2026 represent both opportunities and challenges for QA teams. AI-driven testing, continuous testing practices, shift-left and shift-right testing, expanded automation, and emerging testing types like IoT testing and blockchain testing require new skills, tools, and testing methodologies.
Success in modern software testing requires more than just tools, it demands strategic thinking about how testing integrates throughout the software development lifecycle, investment in team capabilities, and testing platforms that provide visibility across increasingly complex testing activities.
The trends shaping software testing in 2026 emphasize:
- Automation over manual repetition
- Intelligence over brute-force testing
- Continuous validation over periodic checkpoints
- Collaboration over isolated QA teams
- Prevention over detection
- Comprehensive quality over functional correctness alone
These trends like AI testing, continuous testing, and shift-left approaches ensure software quality improves while delivery speed accelerates, the holy grail of software development.
Testomat.io provides a unified platform designed for the current testing landscape and the future of software testing. Whether implementing AI-powered test generation, scaling test automation across multiple frameworks, establishing continuous testing in CI/CD pipelines, or seeking better visibility into testing activities, Testomat.io offers capabilities that support modern testing practices at every scale.
Want to see how these trends apply to your specific context? Schedule a personalized demo at testomat.io to discuss your testing challenges with product experts who understand the latest software testing trends and can show you how Testomat.io addresses them. From AI-powered features to comprehensive CI/CD integration, discover how Testomat.io helps forward-thinking teams ensure software quality in 2026 and beyond.