Through the course of this blog post, we will briefly cover the main points of BDD (Behavior Driven Development) conception. Without going into details, only the most important things.
What is a Behavior?
Behavior is the action and interaction of an individual according to the environment. Simple, it is scenarios. An application or a feature exhibits some scenarios and due to this calls behavioral responses => behaviorlicity.
Examples:
- logging into a web page
- follow the links for navigation
- submitting forms
- receiving expected errors
Different people have different behavior. Sometimes responses depend on particular conditions when doing actions within our examples.
How Different scenarios may lead to the same result. One more example 😀
If you are reading this article, you have found it one of two ways on our site:
- You have found it using the search field, typing here interesting keywords.
- You have found articles using the pagination option on the Blog page.
This approach defines various ways to develop a feature based on appropriate behavior. That is the essence of BDD Agile – adapting user behaviors into flexible development patterns.
What is BDD?
Behavior Driven Development (BDD) is an Agile software development methodology that encourages cooperation between software developers, business stakeholders, QA team, and different roles involved in the project. The main concept is to combine an engineering component with a business goal to succeed, a principle that’s fundamental in BDD in Agile development.
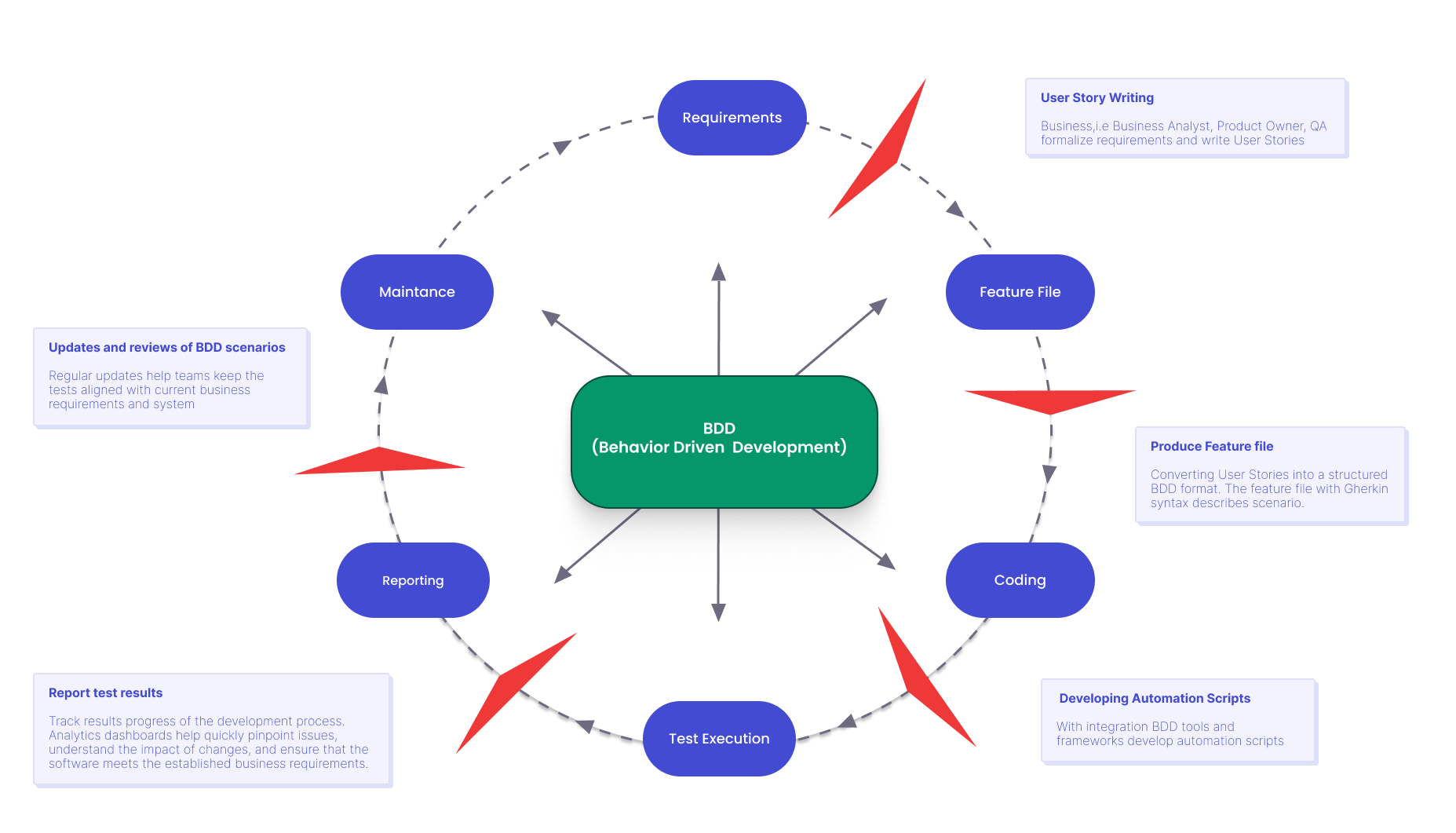
BDD is a test-centred software development approach. Mainly tests are based on desired systems behavior, written in terms of business value. BDD focuses on Test First Development conception. It means a Shift Left Approach because we try to start testing before the development phase.
Behaviour scenarios are the cornerstone of Behavior Driven Development 🪨☘️️
- Scenarios focus on the expected behaviors of the product
- Each scenario focuses on one specific feature
- Scenarios can be run manually (Manual Testing) or automatically (Automation Testing)
User Story
In the BDD Agile development process, requirements should be converted into user stories. Quality Assurance Engineers strive to use a shorter user story format. Business analysts, product owner, and software development team collaborate to ensure a shared understanding of the problem. It’s therefore imperative to adopt a BDD Agile methodology to get all the requirements right from the outset. Mostly, one user story equals one product functionality, a crucial aspect when applying BDD Agile frameworks.
Gherkin BDD
Gherkin is one of the most popular languages describing systems behavior. It represents behaviors as scenarios.
Features are the highest-level description of the desired product functionality.
Feature File is a file that contains one feature. Also it includes information for each feature scenario.
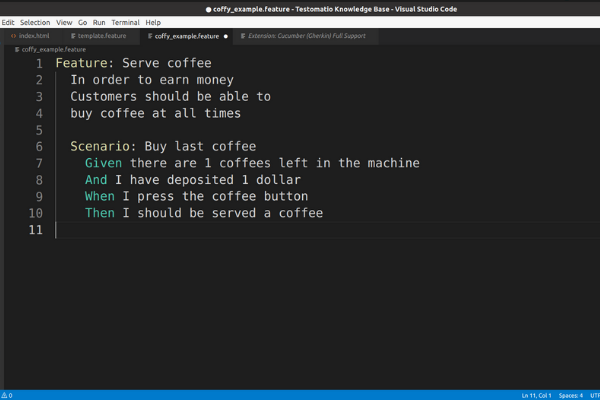
Scenarios answers on ques: Would be? What happens? Why? And what should the application do according to the user story?
Behavioral specifications are formalized expected outcomes, explaining what it they actually does.
GivenThe initial condition. If there are several initial conditions, then each new condition is added from a new line using the And keywordButAnother outcome
| And | Some more context |
|---|---|
| When | The event that initiates this scenario. If the event is complex, then all subsequent details are described within the keywords And and But. |
| Then | This is a verification step, here should be the outcome claimed |
| As a | The role of the person in the business model interested in this feature. |
| I want | Description of feature benefit |
| In order to | Person’s goal |
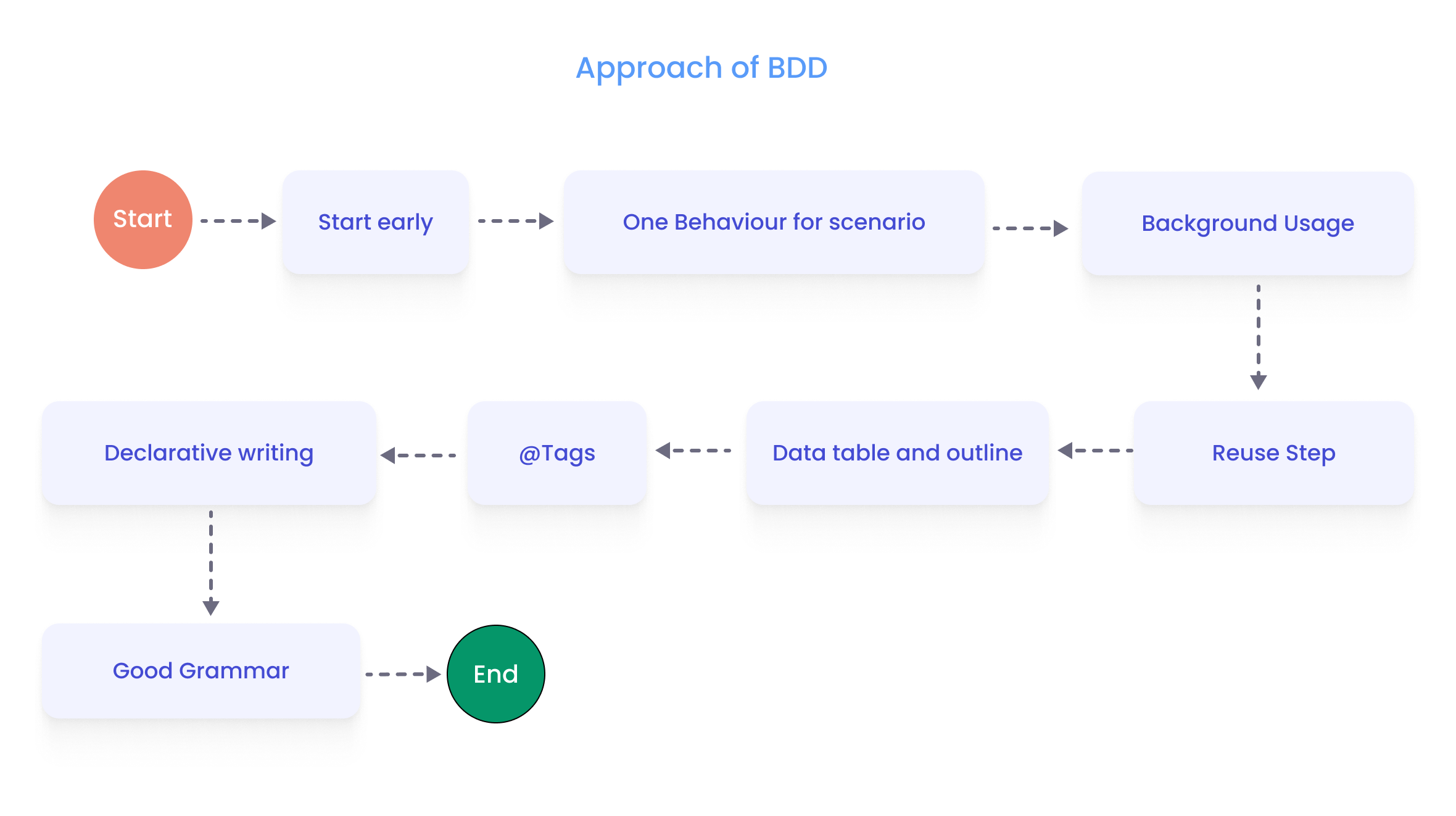
The key goal is to implement in live that not only a Quality Assurance Engineers’ team but anybody from team members, like BA, PO, DEV can write BDD scenarios as well since they are just English phrases.
Key Behavior Driven Development Benefits
- The major benefits of BDD are better team collaboration and shared understanding among stakeholders.
- Customer-oriented, consequently BDD helps to reach a wider user-ends audience, focusing on the business’s needs and user experience. This makes the product more successful.
- With the help of automation tools, Gherkin BDD scenarios can easily be turned into automated test cases.
- Code reusability, you can assign variables.
- Speed up the development process and delivery of the products.
- More reliable outcomes of testing.
- Reducing rework and ambiguity during development.
4 Reasons Why is BDD an Excellent Pair to Agile & Scrum?
- BDD is flexible, changes made easy
- BDD is a refinement of the Agile process, not an overhaul
- It formalizes Acceptance Criteria and Test Coverage
- BDD is like a third layer between business stakeholders and test automation.
Testomat.io supported BDD
- Advanced BDD, Gherkin implementation
- Auto formatting and enhancement in BDD Editor
- Autogenerated living BDD documentation
- Autoconverting classical test cases to BDD test cases
Technology Stack Support:
BDD frameworks and tools support multiple languages like Java, JavaScript, Ruby, and can be integrated with Visual Studio.
BDD plays a crucial role in the software development lifecycle by promoting clarity, reducing compatibility issues, and ensuring product quality at the right time using best practices promoted by organizations like Agile Alliance.
…more details about BDD support
Frequently asked questions
What is BDD?

Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) is a software development methodology that emphasizes collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders to create a shared understanding of the desired behavior of a software system. BDD aims to enhance communication among team members and stakeholders by using simple, domain-specific Gherkin language that simplifies participants’ collaboration.
What is the BDD Process?

Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) follows a structured process. Here is an outline of the BDD process:
- Discovery and Collaboration: engaging all relevant stakeholders, including developers, testers, business analysts, and product owners, to gather and understand requirements.
- Meetings: it is conducting collaborative meetings to discuss and refine user stories and scenarios. This helps ensure that everyone has a shared understanding of the requirements and expected behavior of the system.
- Defining User Stories and Scenarios: user stories writing that describe the desired features from the end user’s perspective. A user story typically follows the format: “As a [role], I want [feature] so that [benefit].”
- Acceptance Criteria: defining a clear acceptance criteria for each user story to specify what conditions must be met for the story to be considered complete.
- Scenarios: break down user stories into specific scenarios using the Given-When-Then format to describe how the system should behave in different situations. Each scenario should cover a distinct aspect of the functionality.
- Choosing Automation Tools: selection of appropriate BDD tools and frameworks, such as Cucumber, SpecFlow, or Behave, to automate the scenarios.
- Continuous Testing: run the automated tests to validate that the implemented features work as expected and that no regressions are introduced.
- Review and Feedback: regularly review of the developed features to stakeholders to gather feedback and ensure alignment with business goals.
- Continuous Improvement: rewriting of user stories, scenarios, and acceptance criteria based on feedback and evolving requirements. Continuously improving the BDD automation process.
- Iterative Development: repeating the process iteratively, refining and expanding the set of user stories and scenarios in each development cycle.
How do BDD and Test Management Interrelate?

Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) and test management are closely interrelated as they both aim to improve the quality of software. Here’s how BDD and test management interrelate:
- Aligns Requirements with Tests
- Promotes collaboration
- Implements traceability and Accountability
- Scenario Definition and Automation
- Track Test Execution
- Reports test results
What to keep In Mind When Getting Started with BDD Testing?

Starting with Behavior Driven Testing involves understanding BDD principles, choosing the right tools, defining clear user stories and scenarios, automating tests, and fostering collaboration among all stakeholders. By keeping these key points in mind, teams can ensure the successful adoption of BDD, leading to improved software quality and better alignment with business requirements.
How to Write Functional Tests for Web Applications?

1. Understanding the Requirements
2. Creation Test Scenarios
3. Choosing the Right Tools
4. Set Up the Testing Environment
5. Preparing test data required for executing the test cases