An e-commerce website that crashes during Black Friday loses thousands of dollars per minute. A confusing checkout page drives customers away every single day. A security vulnerability exposes payment data and destroys years of trust in seconds.
E-commerce testing prevents these disasters. But here’s what most teams get wrong: they treat testing as a checkbox exercise. Run some tests, fix obvious bugs, ship it. Then production breaks under real traffic, customers complain about usability issues nobody caught, and the team scrambles to fix problems that should never have reached users.
Effective e-commerce testing requires a systematic approach. You need to verify that functions work correctly, the site performs under traffic spikes, security protects sensitive data, and the experience works across different browsers and devices. This guide shows you how to test an e-commerce platform properly, which types of testing matter most, when to automate, and which testing tools actually help.
What is e-commerce testing?
E-commerce testing is the process of validating that an online shopping website or application works correctly before customers use it. Testing covers everything from product search functionality to payment processing, from shopping cart behavior to order confirmation emails.
The goal is simple but critical: find and fix problems before customers encounter them. A bug that prevents checkout completion doesn’t just frustrate one user, it blocks every sale until someone fixes it. Testing an e-commerce website means systematically verifying that customers can find products, add them to their cart, complete checkout, and receive their orders without encountering errors or confusion.
E-commerce testing ensures the website can handle real-world conditions. Hundreds of concurrent users during flash sales. Various payment methods from different countries. Shipping addresses in unexpected formats. Discount codes combined with other promotions. Inventory updates while customers are mid-checkout. All the complexity that comes with online retail needs verification before it reaches production.
10 e-commerce testing benefits
Testing might feel like it slows down development, but skipping it costs far more than the time invested. Here’s what thorough testing actually delivers:
- Prevents revenue loss from broken functionality. When the “Add to Cart” button stops working, sales stop immediately. Testing helps identify and fix these critical issues before they reach production. A single hour of downtime during peak shopping can cost major retailers millions in lost revenue.
- Improves customer experience and conversion rates. A thoroughly tested e-commerce site loads quickly, navigates smoothly, and completes transactions without errors. Good experiences lead to repeat customers. Testing that focuses on usability through user interface testing catches the confusing workflows and unclear messaging that cause cart abandonment.
- Protects against security breaches that destroy trust. Security testing finds vulnerabilities before hackers do. Given that e-commerce platforms process payment information and store customer data, security isn’t optional. A single breach can permanently damage reputation and result in massive regulatory fines.
- Ensures compatibility across devices and browsers. Customers shop on phones, tablets, and computers using different browsers. Cross-browser and cross-device testing confirms the site works everywhere. Finding that checkout breaks in Safari on iPad is better discovered in testing than through customer complaints.
- Validates performance under load. Load testing and performance testing reveal whether the website can handle increased traffic during sales events or holiday shopping seasons. Finding capacity limits in testing prevents crashes when traffic spikes matter most.
- Reduces cart abandonment through better usability. Usability testing identifies confusing interfaces or complicated checkout processes that cause customers to abandon purchases. Even small improvements, clearer button labels, fewer form fields, better error messages, can increase conversion rates significantly.
- Confirms payment processing works reliably. Integration testing with payment gateways ensures transactions process correctly. A single payment processing error can cost customer trust permanently. Testing catches integration issues before real money is involved.
- Verifies accurate inventory management. Testing inventory systems prevents overselling out-of-stock items or showing incorrect stock levels. These errors damage customer relationships when people order items they can’t receive.
- Validates order fulfillment workflows end-to-end. Testing the complete order flow from purchase through shipping confirmation ensures the backend processes work correctly. Customers need to receive what they ordered, when promised. Testing catches workflow gaps early.
- Identifies issues before customers do. Every bug found in testing is one fewer complaint, support ticket, or negative review from customers. The cost of fixing issues increases dramatically once they reach production.
What to know before running e-commerce testing
Jumping straight into testing without preparation wastes time and misses critical issues. Understanding your specific context shapes which testing strategies make sense.
Your e-commerce business model determines testing priorities. A B2C fashion site needs a different testing focus than a B2B wholesale platform. Subscription-based services require different test scenarios than one-time purchase stores. Know whether you’re testing B2C retail, B2B wholesale, C2C marketplace, or subscription services. Each model has different critical paths that deserve the most testing attention.
Map the complete customer journey before writing test cases. Document every step customers take from landing on your e-commerce website through receiving their order. This includes finding products through search or categories, viewing product details, adding items to cart, modifying cart contents, entering shipping information, selecting payment methods, completing checkout, receiving confirmation, and tracking orders. Each step needs verification.
Not all features matter equally to your ecommerce business. Payment processing is more critical than wishlist functionality. Prioritize testing based on business impact rather than testing everything equally. Most e-commerce sites have similar critical flows: search and browse, shopping cart operations, checkout process, payment processing, order confirmation, and user account management. These deserve the deepest testing.
Understanding when traffic spikes occur helps you plan performance testing appropriately. Most e-commerce sites see increased load during Black Friday and Cyber Monday, holiday shopping seasons, flash sales and promotional events, and product launches. Performance testing should simulate these conditions, not just average traffic.
E-commerce platforms rarely operate in isolation. List all external services your site depends on: payment gateways like Stripe or PayPal, shipping calculators, tax calculation services, inventory management systems, CRM platforms, and marketing tools. Integration testing must cover all of these connections because failures in third-party services affect your customers directly.
Types of e-commerce testing
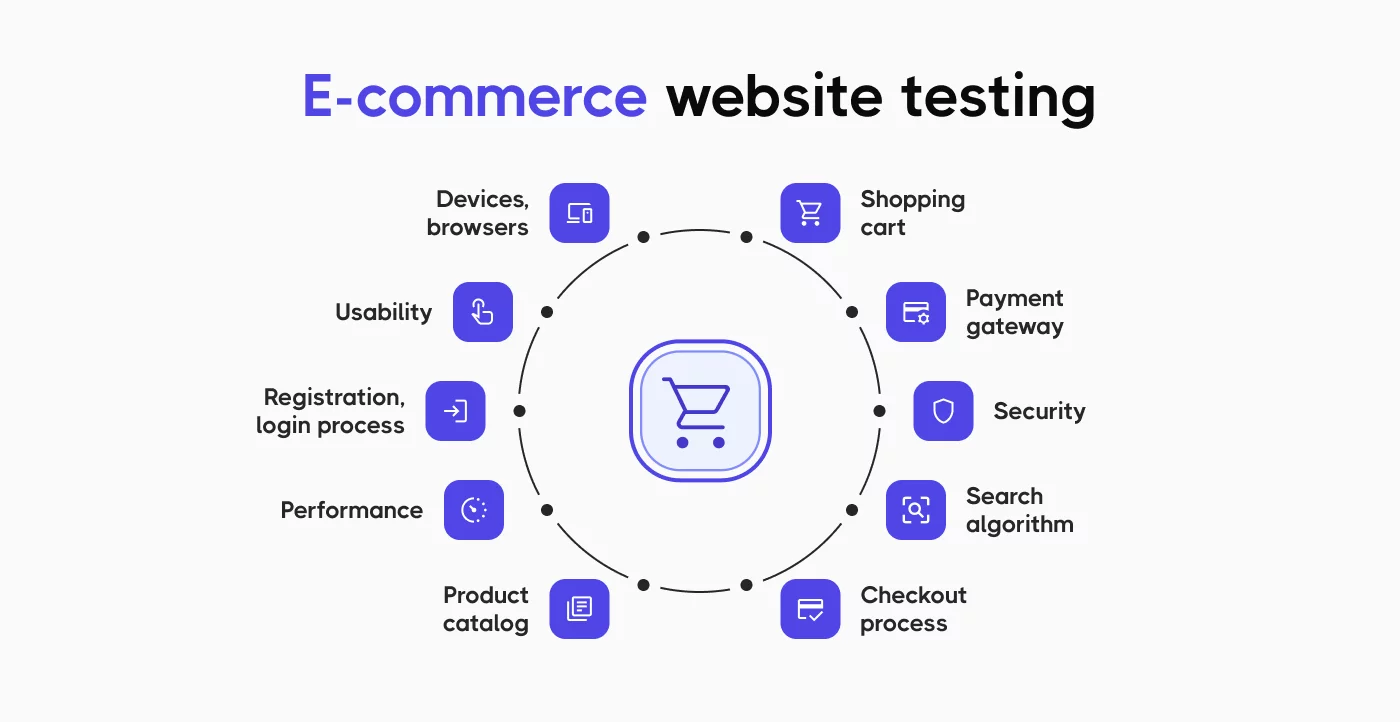
Effective e-commerce testing requires multiple approaches. Each type of testing focuses on different quality aspects. You can’t validate everything through one testing method.
Functional testing
Functional testing verifies that features of the e-commerce website work as specified. This is the most basic type of testing but also the most critical. If core functions don’t work, nothing else matters.
Testing product catalog functionality means verifying that products display with correct information including name, price, description, and images. Product categories need to organize items logically. Filters and sorting must work properly so customers can find what they want. Search needs to return relevant results, not just anything containing the search term. Product recommendations should actually relate to what customers are viewing.
Shopping cart operations require extensive testing because cart issues directly prevent sales. Adding items to cart must work consistently. Quantity updates need to recalculate totals correctly. Removing items should function properly without breaking the cart. Cart contents should persist across sessions so customers don’t lose their selections. Cart totals must be calculated accurately including all discounts and adjustments.
The checkout process is the most critical area for functional testing. Shipping address validation needs to catch errors before orders are placed. Payment method selection must work reliably. Discount code application requires careful testing because promotional logic gets complex. Tax calculation must be accurate based on shipping location. Shipping cost calculation depends on multiple factors that all need verification. The final order total needs to include everything correctly.
User account features enable returning customers to shop efficiently. Registration and login must work smoothly. Password reset functionality helps customers who forget credentials. Order history should display accurately. Address book management lets customers save multiple addresses. Saved payment methods need secure handling. Wishlist operations might be less critical than checkout but still need verification.
Functional testing focuses on whether each feature does what it should. The testing process involves creating specific test cases for each function, executing those tests systematically, and documenting which features work correctly and which have defects.
Usability testing
Usability testing evaluates how easy and intuitive the e-commerce site is to use. Even if all functions work correctly, poor usability loses sales. Customers won’t struggle with confusing interfaces when competitors are one click away.
Navigation clarity determines whether customers can find products efficiently. Can they locate items without frustration? Are menu structures logical or do they hide important categories? Do breadcrumbs help customers understand where they are on the site? Is the search feature prominent and effective, or buried where nobody finds it?
Interface design affects conversion rates more than most teams realize. Buttons need clear labeling so customers know what happens when they click. Call-to-action elements must stand out visually. Important information should be visible without scrolling on key pages. Forms need to be simple to complete without unnecessary fields that annoy customers.
Checkout flow usability directly impacts cart abandonment. How many steps does checkout require? Is progress clearly indicated so customers know how much longer the process takes? Can customers edit information easily if they notice an error? Are error messages helpful or just frustrating?
User interface testing often reveals that features work technically but frustrate customers in practice. A checkout process that requires 10 steps might function perfectly from a technical perspective but causes cart abandonment because customers give up. This is why usability testing involves actual users attempting realistic tasks while observers watch for confusion and friction.
Performance testing
Performance testing evaluates how fast the e-commerce website responds and whether it maintains speed under various load conditions. Speed affects both customer experience and search engine rankings.
Load testing simulates multiple concurrent users to see how the website handles increased traffic. This type of testing is crucial before peak shopping seasons. You need to know whether your site can actually handle Black Friday traffic before Black Friday arrives.
Run load tests that simulate normal traffic to establish baseline performance, expected peak traffic to match your busiest days, and beyond-peak traffic to identify stress points. Measure page load times under load, transaction completion rates, server response times, database query performance, and API response times. All of these metrics matter because slow performance anywhere in the stack affects customers.
Stress testing pushes the e-commerce platform beyond normal capacity to find breaking points. This reveals what happens when traffic exceeds your predictions. At what point does the site slow down noticeably? When do errors start appearing? How does the system fail, gracefully with helpful messages, or catastrophically with blank pages? How quickly does the site recover after traffic drops?
Scalability testing ensures the website can handle growth over time. As your ecommerce business expands, the platform must scale accordingly. Test whether the system maintains performance when the product catalog grows from 1,000 to 10,000 items, when the customer base increases 10x, when order volume doubles, or when traffic spikes unexpectedly.
Scalability testing ensures the website can handle increased traffic and transaction volumes without degrading performance. This becomes critical as successful e-commerce businesses grow rapidly.
Security testing
Security testing identifies vulnerabilities that could expose customer data or allow unauthorized access. For e-commerce software testing, security testing is absolutely not optional. The cost of a security breach far exceeds any testing investment.
Payment security requires the highest attention. You must verify PCI DSS compliance for payment data handling. Credit card information needs encryption during transmission and secure storage. Payment gateway integration must be secure without leaking sensitive data. CVV validation should work properly. Fraud detection mechanisms need testing to ensure they catch suspicious transactions without blocking legitimate customers.
User authentication protects customer accounts from unauthorized access. Password strength requirements need enforcement. Secure password storage using proper hashing is essential, never store plaintext passwords. Protection against brute force attacks prevents hackers from guessing passwords. Session management must be secure to prevent session hijacking. Multi-factor authentication adds protection for high-value accounts.
Data protection extends beyond payment information. SSL/TLS encryption needs to cover all pages, not just checkout. Customer information requires encryption both in transit and at rest. GDPR and other privacy laws have specific requirements for data handling. Backup procedures must be secure so archived data doesn’t become a vulnerability.
Common vulnerabilities need systematic testing. SQL injection prevention stops attackers from accessing your database. Cross-site scripting (XSS) protection prevents malicious code injection. Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) prevention protects against unauthorized actions. Secure file upload handling prevents attackers from uploading malicious files. Protection against DDoS attacks helps maintain availability during attacks.
E-commerce testing ensures that customer trust isn’t violated through preventable security gaps. Security testing is a critical ongoing process, not a one-time check.
Compatibility testing
Compatibility testing verifies the e-commerce website works correctly across different environments. Customers use varied devices, browsers, and operating systems. Your site must work on all of them or you’re turning away customers.
Cross-browser testing checks major browsers customers actually use. Test on Chrome desktop and mobile, Safari desktop and mobile, Firefox, Edge, and Samsung Internet for Android users. Verify that layout renders correctly, JavaScript functions work, CSS applies properly, forms submit successfully, and checkout completes. Browser compatibility issues cause real revenue loss when customers can’t complete purchases.
Cross-device testing covers the hardware customers use. Test on desktop computers with various screen sizes, tablets including iPad and Android tablets, and smartphones including both iPhone and Android phones at different screen resolutions. Check that responsive design adapts properly, touch interactions work on mobile devices, images scale appropriately, text remains readable, and buttons are easily tappable with fingers.
Operating system compatibility matters because behavior varies across platforms. Verify functionality on Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, and Linux for B2B customers who might use it. Some issues only appear in specific OS and browser combinations.
Cross-browser and cross-device testing catches display and functionality issues that only appear in specific environments. Testing on just one browser and device misses problems that affect significant portions of your customer base.
Test cases for e-commerce website
Creating comprehensive test cases ensures nothing important gets overlooked. Test cases for an e-commerce website need to cover all critical functionality systematically.
- Start with product search and browsing. Test that searching with a valid product name returns correct results. Verify that search with a partial name shows helpful suggestions. Check that category navigation displays the correct products without including items from other categories. Confirm that filters reduce results appropriately when customers apply price ranges or other criteria. Validate that sorting changes product order correctly.
- Shopping cart operations need thorough test coverage because cart problems directly prevent sales. Verify that adding a product to cart updates the cart count immediately. Test that updating quantity recalculates the cart total accurately. Confirm that removing an item from cart works correctly and adjusts totals. Check that cart contents persist after logout so customers don’t lose their selections. Validate that an empty cart displays an appropriate message and suggestions.
- The checkout process deserves the most detailed test cases. Test that guest checkout allows purchase without forcing account creation. Verify that shipping address validation catches errors like invalid ZIP codes before processing. Confirm that customers can manage multiple shipping addresses. Test that payment method selection works for all supported options. Verify that discount codes apply correctly and invalid codes show clear error messages. Check that tax calculation is accurate based on shipping location. Validate that order confirmation displays all details correctly. Confirm that confirmation emails send automatically with complete order information.
- User account features enable repeat customers to shop efficiently. Test that new user registration works and send welcome emails. Verify that login with correct credentials succeeds. Check that password reset functionality works end-to-end. Confirm that order history displays past purchases accurately. Validate that saved addresses can be edited and change save correctly.
- Payment processing requires careful testing with various scenarios. Test that valid credit cards process successfully. Verify that invalid card numbers are rejected with clear error messages. Check that expired cards are declined appropriately. Test that PayPal or other alternative payment integrations work correctly through the entire flow.
For e-commerce mobile app testing, add tests specific to mobile functionality. Verify that push notifications work correctly for order updates. Check that biometric login functions properly using fingerprint or face recognition. Test that offline mode handles network loss gracefully.
General test cases for ecommerce websites form the foundation, but you’ll need to customize them based on your specific features and business model.
Automating e-commerce testing
Manual testing catches many issues but becomes unsustainable as the e-commerce platform grows and releases happen more frequently. Automation testing helps maintain quality while shipping updates rapidly.
Why automate e-commerce testing?
Automated tests run much faster than manual testing. What takes a tester 8 hours to test manually might run in 30 minutes automated. This speed enables testing with every code change rather than just before major releases.
- Consistency is another major advantage. Automated tests execute exactly the same way every time. Manual testing varies based on tester attention, fatigue, and interpretation of test cases. When you automate testing, you get reliable, repeatable results.
- Regression testing becomes practical with automation. As features accumulate over months and years, manually retesting everything before each release becomes impossible. Automated regression testing verifies that new changes didn’t break existing functionality without requiring days of manual effort.
- Continuous testing in development pipelines requires automation. Every code commit can trigger tests, providing immediate feedback to developers. This rapid feedback loop catches bugs while the code is fresh in developers’ minds, making fixes faster and easier.
- Cost reduction happens over time with automation. Automated tests require upfront investment in creation and maintenance, but reduce long-term testing costs significantly. Once created, automated tests run repeatedly with minimal cost compared to manual testing.
When to automate e-commerce testing?
Don’t try to automate everything immediately. Focus automation where it provides the most value and keep manual testing for areas where humans excel.
- Regression tests that run before every release are excellent automation candidates. Core functionality verification that happens repeatedly benefits from automation. Tests for previously fixed bugs should be automated to prevent regression. These scenarios run frequently enough that automation pays off quickly.
- Smoke tests that verify critical paths make sense to automate. Basic functionality checks and tests that run on every build catch major breaks immediately. Automated smoke tests give quick confidence that nothing is catastrophically broken.
- Data-driven tests that need multiple input combinations benefit from automation. Testing payment processing with various card types or shipping calculations for different locations becomes tedious manually but is straightforward to automate.
- Performance tests including load testing scenarios, stress testing under heavy traffic, and scalability testing require automation. You can’t manually simulate 1,000 concurrent users.
Keep manual testing for exploratory work where testers find unexpected issues through creative investigation. Usability evaluation requires human judgment about subjective user experience and visual design assessment. Accessibility testing often needs human evaluation with assistive technologies. One-time tests for features that won’t be tested repeatedly aren’t worth automating.
The balance between manual and automated testing depends on your team size, release frequency, and application complexity.
E-commerce testing tool: Testomat.io
Managing test cases, tracking execution, and coordinating between manual and automated testing becomes complex as your ecommerce business grows. Testomat.io is a test management platform designed specifically for organizing and executing comprehensive testing of e-commerce websites and applications.
Why Testomat.io is the best tool for e-commerce testing
Most teams struggle with scattered test documentation, unclear test coverage, and disconnection between manual testing and automated testing. Testomat.io solves these problems by providing a unified platform for the entire testing process.
- Organizing test cases systematically is the foundation. Create test suites organized by feature area like search, cart, and checkout. Group tests by testing type including functional testing, performance testing, and security testing. Organize by device or platform to track web, iOS, and Android coverage separately. Prioritize tests as critical, high, medium, or low based on business impact. Store all general test cases for e-commerce websites in one accessible repository where the entire team can find them.
- Tracking manual testing execution becomes straightforward. Assign test cases to team members for specific testing cycles. Track execution status in real-time on dashboards showing what’s tested, what’s pending, and what failed. Log defects directly from failed tests without switching tools. Generate test reports automatically without manual compilation. This is perfect for usability testing and exploratory testing where human judgment is essential.
- Integration with automated test results is where Testomat.io excels compared to traditional test management tools. Connect automated tests from Playwright, Cypress, and Selenium for web testing. Integrate Appium results for mobile testing. Pull in Postman results for API testing. Actually, any testing framework can integrate via the API. Automated test results flow into Testomat.io automatically, providing complete visibility into both manual and automated testing coverage in one place.
- AI-powered test case generation accelerates test creation significantly. Input your feature requirements or user stories. The AI suggests relevant test cases based on the description. It generates detailed test steps and expected results automatically. The system identifies missing test coverage by analyzing what exists versus what should be tested. This saves hours of manual test case writing, especially when launching new features or expanding to new markets.
- Requirement traceability connects tests to business needs. Link test cases directly to user stories in Jira. Display test execution status right in Jira so product managers see testing progress. Track which features have adequate test coverage and which need more testing attention. The full traceability ensures every requirement has corresponding test cases, which is critical for compliance and quality assurance.
- Collaboration features keep teams aligned. Team members can comment on test cases to discuss edge cases or clarify expected behavior. Use @mentions to notify specific people about test issues needing attention. Shared dashboards give everyone visibility into testing progress. Real-time updates mean nobody works from outdated information. Email notifications alert team members when tests are assigned or completed.
Tips on choosing the right testing tools
When selecting testing tools for your e-commerce platform, consider several factors beyond just features and price.
- Integration with your tech stack is critical. Does the tool support your programming languages for test automation? Can it test your mobile apps if you have them? Does it connect with your CI/CD pipeline for continuous testing? Can it integrate with Jira, GitHub, or whatever tools your team already uses?
- Learning curve affects how quickly your team becomes productive. Is the tool intuitive enough that testers can start using it immediately? Is documentation comprehensive with good examples? Are there training resources or tutorials available? A powerful tool that nobody uses is worthless.
- Cost structure matters more as teams grow. Per-user pricing becomes expensive as teams scale. Team-based or project-based pricing is more predictable. Check whether there’s a free tier for trying before committing. Calculate the actual cost at your expected team size, not just the advertised starting price.
- Community and support determine whether you’ll get help when stuck. Is there an active user community answering questions? Does the vendor offer responsive support? Are there regular updates and improvements to the product? Tools that stagnate become liabilities.
- Scalability is important for growing ecommerce businesses. Can the tool handle your test case volume as it grows from 100 to 1,000 to 10,000 test cases? Does performance remain good with large test suites? Will it grow with your ecommerce business without requiring migration to a different tool?
Testomat.io addresses these requirements specifically. Team-based pricing rather than per-user makes it affordable as teams grow. Comprehensive integrations with popular testing frameworks and development tools. Strong support across all time zones. Regular feature updates including cutting-edge AI capabilities. The platform is designed to scale from small startups to large enterprises.
E-commerce testing best practices
Following proven practices makes testing more effective and sustainable. These aren’t theoretical ideals but practical approaches that work in real e-commerce testing.
- Test early and often rather than waiting until features are complete. Test during development while code is still fresh and changes are easy. Early testing finds issues when they’re cheaper and faster to fix. Catching a usability problem in design mockups is much better than finding it in production.
- Prioritize testing based on risk rather than treating everything equally. Payment processing deserves more testing attention than footer links. Features that handle customer data need more security testing than static content pages. Focus testing effort where failures have the biggest business impact.
- Use production-like data in testing instead of placeholder data. Testing with “John Doe” at “123 Test Street” misses issues that appear with real-world data. Use realistic customer names, addresses, and products. Anonymize actual production data if necessary, but make it realistic.
- Test on real devices, not just emulators. Browser emulators and device simulators help but don’t replace testing on actual phones and tablets. Device-specific issues, especially around payment processing and forms, only appear on real hardware.
- Automate regression testing but keep exploratory testing manual. Use automation for repetitive checks that verify existing functionality still works. Save human testers for exploratory testing where creativity and intuition find unexpected issues that scripted tests miss.
- Monitor production even after testing passes and release happens. Testing doesn’t end at deployment. Monitor production systems for errors, performance issues, and user behavior that indicates problems. Real user monitoring often finds issues that testing missed.
- Include accessibility testing in your regular process. Test with screen readers and keyboard navigation. Accessible sites serve more customers and often perform better for everyone. Many accessibility issues are also usability issues affecting all users.
- Test localization thoroughly if you serve multiple regions. Verify translations are correct and make sense in context. Test currency conversion with real exchange rates. Confirm date and time formats match regional expectations. Check address format requirements for different countries.
- Document test cases clearly so anyone on the team can execute them. Clear test cases enable new team members to contribute quickly, ensure consistent test execution, and make creating automation easier later.
Review and update tests regularly because test cases decay as features change. Schedule quarterly reviews to remove obsolete tests, update tests for changed functionality, add tests for new features, and improve test cases that are unclear or incomplete.
Final thoughts
E-commerce testing is a critical part of running a successful online store, not a luxury or optional activity. Testing an e-commerce platform thoroughly prevents revenue loss from bugs, protects customer data through security testing, ensures performance during peak traffic when it matters most, and creates better user experiences that convert browsers into buyers.
The types of ecommerce testing covered in this guide, functional testing, usability testing, performance testing, security testing, and compatibility testing, each address different aspects of quality. Comprehensive testing requires all of them working together. Focusing only on functional testing while ignoring performance means customers will encounter slow pages during sales. Checking functionality while skipping security testing leaves vulnerabilities for hackers to exploit.
Both manual and automated testing have important roles. Manual testing excels at exploratory work and usability evaluation where human judgment is essential. Automation testing enables rapid regression testing and continuous testing in development pipelines without consuming all your QA team’s time.
Testing tools like Testomat.io make the entire testing process manageable. The platform handles everything from organizing test cases through tracking manual execution to integrating automated test results. The AI-powered test generation helps teams create comprehensive test coverage faster. The unified view of manual and automated testing prevents the common problem of maintaining separate, disconnected systems.
Start with the critical test cases for your checkout flow and payment processing since these directly affect revenue. Expand testing coverage gradually rather than trying to test everything at once. Automate stable test scenarios that run repeatedly. Monitor results and continuously improve your testing strategies based on what you learn.
An e-commerce website that works reliably, performs well under load, protects customer data, and provides a smooth user experience wins customer trust and drives business growth. That’s exactly what thorough testing delivers. The investment in proper testing pays back many times over through prevented outages, caught security issues, and improved conversion rates.
Frequently asked questions
What is ecommerce testing?

Ecommerce testing is the process of validating that an online shopping website or application functions correctly, performs well under load, remains secure from attacks, and provides a good user experience across different devices and browsers. Testing covers product search, shopping cart, checkout, payment processing, and all other functionality customers use.
How to test an ecommerce product?

Test an ecommerce product by verifying functional requirements work correctly, checking performance under expected traffic loads, validating security measures protect customer data, confirming compatibility across browsers and devices, and evaluating usability through actual user testing. Create specific test cases for each area and execute them systematically.
What are the 3 C's of ecommerce?

The 3 C’s of ecommerce typically refer to Content, Commerce, and Community, though in testing contexts, teams often focus on Compatibility, Coverage, and Consistency of testing across platforms to ensure quality.
What are the 4 types of e-commerce?

The four main types of e-commerce are B2C (business to consumer like Amazon), B2B (business to business like wholesale platforms), C2C (consumer to consumer like eBay), and C2B (consumer to business like freelance marketplaces). Each type requires different testing focuses based on the business model.
Are there tools for testing ecommerce websites?

Yes, Testomat.io is a comprehensive test management platform designed specifically for organizing and executing test cases for ecommerce websites. It supports manual testing execution, automated testing integration with frameworks like Playwright and Cypress, AI-powered test case generation, and provides unified visibility into all testing activities.
How can I prepare my eCommerce platform for peak shopping seasons like Black Friday?

Prepare through load testing that simulates expected traffic levels at least 2-3 weeks before the event. Run stress testing to find breaking points beyond your traffic predictions. Perform scalability testing to ensure the website can handle increased traffic without degradation. Have contingency plans ready including additional server capacity and rollback procedures if issues appear.
How can I validate the end-to-end order flow of an e-commerce platform?

Create test cases that walk through the complete customer journey from product discovery through order delivery confirmation. Test both happy paths where everything works and error scenarios where things go wrong. Use both manual testing to evaluate usability and user experience, and automated testing for regression coverage that runs with each release.
How can I verify the performance of an e-commerce website?

Use load testing tools to simulate multiple concurrent users performing realistic actions. Measure page load times, transaction completion rates, and server response times under various traffic levels. Performance testing should include normal traffic baselines, peak traffic scenarios matching your busiest days, and stress tests beyond expected loads.
How do I manually test an e-commerce website?

Follow a systematic testing checklist covering product search and browsing, shopping cart operations, checkout process, payment processing, user account features, and post-purchase flows. Execute test cases methodically, document results in a test management tool like Testomat.io, and log any defects found. Use real browsers and devices that match your customer base rather than just testing on one configuration.