The implementation of Agile and DevOps introduces the need for a fast delivery that traditional testing methods fail to meet. To fulfill this need, Continuous Testing (CT) can be utilized in modern pipelines because of its ability to perform automated quality checks at every stage of software delivery. With the shift-left validation approach of CT, teams can start testing code immediately after writing, instead of postponing testing until the QA phase.
Thus, it helps them detect bugs early and save money on remediation work while making it easier to fix defects. Furthermore, Continuous Testing enables them to develop high-speed software through direct feedback integration in CI/CD workflows, which results in stable system delivery. In the article below, you can find principles, components, and practical steps for implementing a continuous testing strategy in DevOps.
Importance of Continuous Testing in DevOps
With the increasing complexity of applications and the demand for faster releases, the traditional testing approach at the end of the development cycle is no longer sufficient. Thanks to continuous testing integrated into every stage of the CI/CD pipeline, the testing process turns into an ongoing activity, which allows teams to catch defects early and reduce the risk of costly issues in production.
The main reason continuous testing stands as a vital practice is because it delivers quick feedback to developers. While the traditional testing approach delivers code quality and functionality feedback only at the end of the development process, which results in extensive rework, the immediate feedback of continuous testing enables software engineers to fix problems after making any code modification. Not only does it enable developers to build software faster, but it can also simultaneously enhance the final software product quality.
What is Continuous Testing?
Continuous Testing is applied by the teams to run automated tests after each code modification to deliver immediate feedback as part of the software delivery pipeline. This testing method enables developers to detect problems immediately after code changes so they can notify others and perform repairs.
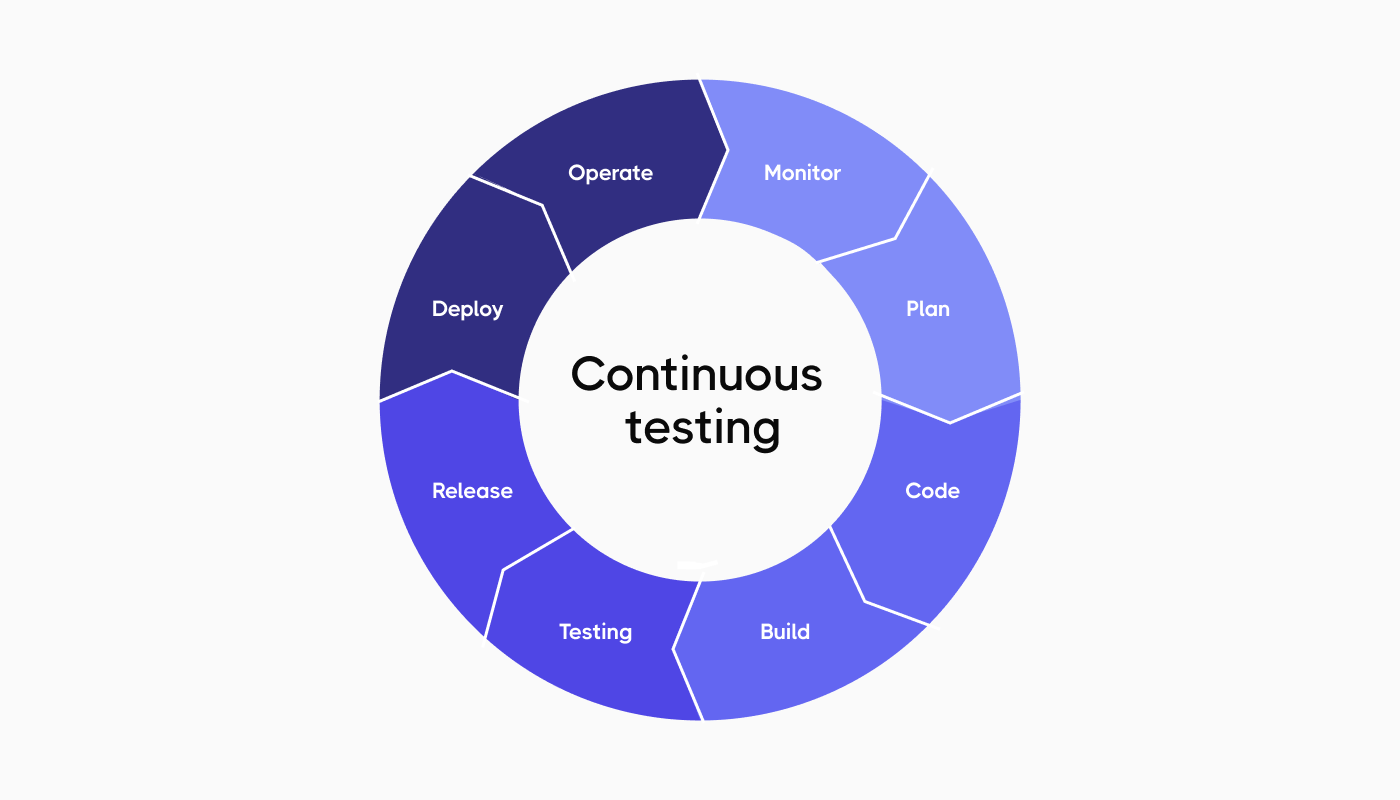
The testing process aims to execute tests at shorter intervals, which begin with assessments of the single components before moving to complete codebase testing.
It is important to mention that the Continuous Integration (CI) process in Agile and DevOps pipelines depends on continuous testing to deliver software at a faster pace with enhanced efficiency.
How does continuous testing differ from traditional software testing?
The following comparison between Continuous Testing in DevOps and Traditional Testing demonstrates the fundamental change in testing approaches:
| Aspect | Continuous Testing in DevOps | Traditional Testing |
| Timing | It occurs continuously throughout all development stages after each code modification (Shift-Left). | It runs independently during its final stage when most development work has already been finished (End-of-Cycle). |
| Automation | It depends on automated systems to perform its fast repetitive tasks. | It requires manual work for extensive periods because automation tools are not always used. |
| Feedback | It produces results through code modifications within a short period of time. | It delivers feedback at a distant point, which results in bugs that become expensive to fix and require complex solutions. |
| Integration with DevOps | It operates as a fundamental component of CI/CD pipelines and DevOps systems. | It fails to connect properly with the fast-paced requirements that modern DevOps operations need. |
| Speed and Efficiency | It operates at high speed to support fast release timelines. | It operates at a slower pace because it functions as a bottleneck when performing manual testing at full capacity. |
| Risk Mitigation | It detects problems early and often during development, which minimizes overall risk throughout the process. | It detects bugs at a later stage, which raises the probability of production system failures. |
| Culture and Collaboration | It promotes team collaboration between Development and QA, and Operations teams for shared quality responsibility. | QA teams are responsible for software quality. |
Core Principles of Continuous Testing
The adoption of Continuous Testing needs more than new tools because it requires teams to transform their entire quality assurance approach. Organizations need to follow four essential principles to successfully integrate testing into their DevOps:
Shift Left
The development process should include testing as an essential component instead of waiting for the “testing phase”. The “Shift Left” approach requires testing to start at requirements development and continue through the entire coding process. The process of validating ideas and code at early stages helps teams detect defects at their most affordable cost point for efficient correction before technical debt builds up.
Automation
Manual testing cannot scale at DevOps speed. Teams need to automate their entire testing suite, which includes unit and integration tests, regression and performance checks, to achieve continuous feedback. The system performs complete safety checks on every code commit through automated processes without requiring human involvement.
Actionable Feedback Loops
The main objective of Continuous Testing involves providing instant business risk assessments. Testing tools need to deliver instant, understandable results to developers. The system should stop execution when tests fail while delivering exact details about the failure causes to developers for quick problem-solving.
Seamless Integration
Testing requires a unified approach because it needs to operate as a total system that is fully integrated with the CI/CD pipeline. The testing process requires dynamic environment provisioning through containerization and immediate access to test data for successful execution. If done correctly, the system eliminates resource-related delays, which enables continuous development-to-production flow.
Integrating Continuous Testing into the CI/CD Pipeline
The DevOps pipeline depends on Continuous Testing to function because it operates directly with Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) as its core elements. While the main function of CI is to maintain application stability and consistency during development for accelerated development cycles and enhanced software quality, the aim of CD is to speed up automated release processes, which keeps the codebase continuously available for deployment.
Let’s take a look at how the Continuous Testing process operates throughout the two essential stages of the pipeline:
| Feature | CI Stage (Continuous Integration) | CD Stage (Continuous Delivery/Deployment) |
| Goal | It has a focus on checking that new code submissions do not damage the build process or create fundamental logical problems. | It verifies that the application operates correctly in a simulated production environment while fulfilling user needs. |
| Responsibility | Developers who maintain unit tests perform immediate bug fixes after each code commit. | QA Engineers take responsibility for coordinating intricate E2E scenario execution and performance testing suites. |
| Scope of Testing | It examines individual components, functions and classes separately from other system elements. | It examines the complete system through API communication, database connectivity, and user interface functionality. |
| Key Test Types |
|
|
| Environment | The build process uses temporary containers, which exist only for testing purposes. | The testing environment duplicates production conditions. |
| Execution Speed | The testing process needs to remain lightweight because it should deliver instant results to developers. | Tests include detailed simulations, which mimic actual user interactions and system loading behavior. |
| Results |
|
|
Key Components of Adopting Continuous Testing
- Automated Test Scripts. The development team uses these tests to run automatically during their testing and development work.
- Test Environment Management. The test environment needs to duplicate the conditions, which exist in production operations.
- Test Data Management. The process of creating, storing and handling test data for automated testing operations.
- Testing Frameworks. The testing frameworks enable teams to perform different test types, including unit testing, integration testing, performance testing, security testing, and regression testing.
- Pipeline Orchestration. The CI/CD lifecycle receives automated build, test and deployment stage management through pipeline orchestration to perform quality checks for every change to achieve quick, reliable, and consistent release.
- Acceptance of TDD and BDD. Teams that adopt TDD and BDD can specify expected behavior before coding, which results in better understanding between stakeholders and in producing high-quality testable software during development.
- Feedback. The system provides instant test results, which help developers detect problems and defects during the initial development stage.
Steps for Implementing a Continuous Testing Strategy
Here’s how you can successfully implement a continuous testing strategy that aligns with your DevOps pipeline:
Define clear testing purposes
The development process requires development and QA teams to establish particular testing targets for each development phase. The testing process requires identification of test types, including unit tests, integration tests, functional tests, performance tests and security tests, along with quality standards to reach. You also need to note that the testing objectives become clear when they match the project targets.
Here are some examples of testing purposes:
- Detect and fix defects during the early stages of development with the shift-left testing method.
- Reach at least 84% automated test coverage to meet requirements.
- Eliminate all critical security vulnerabilities through automated security testing integration.
- Guarantee that the app responds within 500 milliseconds and meets performance requirements.
- Achieve a 99.99% success rate to provide stable and reliable software delivery.
Select the right testing tools
DevOps pipelines need different testing tools to perform automation testing, execute tests and monitor results. The following tools serve as recommended solutions:
- Version control systems for managing source code (Git).
- CI/CD automation tools for automating build and test processes (Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab, CI).
- Test management tools for handling all stages of testing operations (Testomat).
- Performance testing for simulating traffic and load conditions ( Apache JMeter).
- Functional testing for performing UI and browser automation. (Selenium, Cypress).
- API testing for testing API endpoints and performance (Postman, JMeter).
- Security testing for detecting security vulnerabilities (OWASP ZAP, Burp Suite).
- Test environments for creating production-like environments for validation purposes (Docker, AWS).
Integrate test automation in CI/CD pipelines with Quality Criteria
Agile teams must perform sprint-based testing for new features and functionality while maintaining ongoing verification of their existing functionality. The process of regression testing requires extensive automation because it needs to be performed efficiently. Your CI/CD pipelines require test automation integration through the following steps:
- Write or generate test cases for unit, integration, functional, and security testing.
- Automatically run test suites and execute them continuously across different platforms.
- Parallelize tests to reduce execution time.
- Produce complete run reports for analysis.
Teams also need to implement Quality Criteria, which function as essential checkpoints to defend the pipeline through strict requirements that code needs to fulfill before it can merge or deploy. Here are some examples of specific targets:
- Achieving 80% code coverage
- Obtaining a 95% test success rate
- Security verification through OWASP checks.
When any quality criteria fail, the pipeline execution stops immediately and blocks the deployment due to defective or insecure code.
Establish Real-Time Feedback and Notification
Your testing process needs to run automatically whenever developers make code changes. The development team should receive immediate test failure alerts through instant notification systems, which enable them to fix defects quickly. It can be done by:
- Setting up notifications for developers about test failures and build problems.
- Tracking test results through Testomat.io and other monitoring tools.
- Real-time monitoring of response times, resource utilization, error rates and security vulnerabilities.
- Performing scheduled assessments of feedback data and performance metrics.
Only by implementing a notification system to alert your team about test failures and issues can you respond immediately and solve problems efficiently.
Measure, Report, and Optimize Continuously
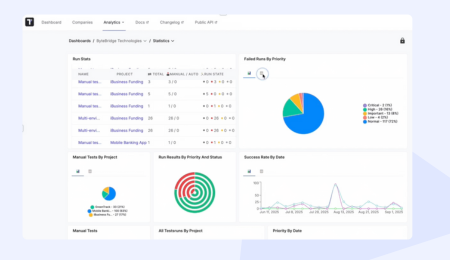
A sustainable, continuous testing strategy requires visibility and adaptivity to function properly. The test results require teams to examine complete reports, which show pass/fail tests through visual dashboards. The detailed reports enable teams to monitor test outcomes together with code coverage statistics and essential performance indicators, providing full transparency to technical teams and project stakeholders. Thus, they must regularly inspect these metrics for ongoing improvement and optimization to identify operational delays and insufficient coverage areas that match project development requirements.
Benefits of Continuous Testing in DevOps
Let’s overview some benefits when you implement continuous testing into your DevOps pipeline:
- Software and QA engineers can dedicate their time to solving intricate problems because automation handles repetitive work, which accelerates feature delivery and allows for rapid, successful releases.
- Development and QA teams that implement early defect detection during development cycles minimize their costs and work needed to resolve problems, which would otherwise grow more complicated in later development stages.
- The development process maintains high code quality and stability because continuous testing performs immediate checks on every code modification.
- The DevOps pipeline requires testing integration, which creates a natural environment for development and QA teams to collaborate and establish essential quality ownership responsibilities.
- The software maintains its reliability and stability throughout the development cycle because continuous testing prevents commercial risks from deploying unstable or faulty code to production.
- Automation technology enables organizations to perform extensive testing of complex applications, which would be impossible to execute through manual methods, thus resulting in enhanced test coverage.
Why use Testomat.io for Continuous Testing in DevOps?
- Testomat.io TMS enables native integration with Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and GitLab CI/CD pipelines to provide instant build health visibility through test result synchronization.
- TMS unifies test results from different automation frameworks, including Cypress, Playwright and Selenium into one dashboard, which shows both automated and manual testing information.
- TMS identifies unstable tests through automated processes, which enables teams to identify and monitor these tests throughout time for better deployment pipeline reliability.
- TMS generates human-readable descriptions from automated test scripts, which maintains perfect alignment between business requirements and testing documentation and current code versions.
- TMS provides real-time analytics, which helps teams measure test execution speed and failure patterns to enhance their testing approach and decrease development time.
In addition to that, Testomat.io uses AI technology in continuous testing to boost test design speed, execution optimization, and enhance pipeline stability. The AI converts traditional test management work into an automated process through its smart workflow system:
- It generates complete test cases, steps, and descriptions through its analysis of current tests and Jira user stories, and plain text requirements.
- It identifies unstable tests throughout multiple test runs and enables teams to focus on critical fixes, which enhance their CI/CD pipeline stability.
- It processes test execution logs to detect patterns in test failures, which it uses to identify clusters of similar issues and determine their original causes.
- AI agents evaluate current test suites to detect duplicate tests and recommend improvements for complex tests, and identify missing test areas.
- It determines test priority based on risk levels to achieve maximum defect detection through the execution of essential tests within a limited time frame.
Bottom Line
Today’s organizations need to make Continuous Testing their default practice in order to reach DevOps maturity. Turning traditional testing into an automated process enables teams to prevent bugs instead of detecting them. That is why the integration of quality assurance directly into the development lifecycle allows teams to build a collaborative workflow and produce strong release pipelines, which deliver fast software with superior user experiences. If you have any questions, don’t hesitate to contact us today for a consultation on how to use Testomat.io to connect test management functions to support your continuous testing initiative.