Behaviour-Driven Development (BDD) allows seamless collaboration among QA testers, developers, and business stakeholders during the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), ensuring alignment of testing efforts with business requirements. The test management system testomat.io enables teams to create, manage, and execute BDD tests, and it natively supports the Gauge test automation framework.
What is Gauge Framework?
Gauge is a lightweight and flexible open-source testing framework for writing and running E2E tests. It helps teams write maintainable acceptance tests in plain, readable language while still being backed by powerful automation code.
What is a Gauge Specification?
Gauge specification is the definition of test cases, which are in a simple Markdown-like syntax (typically in .spec or .md files).
In software testing and development, a specification is a detailed human-readable description of how a system, feature, or functionality should behave.
Characteristics of good specification:
- Readable. Written in plain language, fostering collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders.
- Executable. Steps link to code implementations, enabling automation.
- Data-Driven. Supports tables or external files (e.g., CSV) for testing multiple scenarios efficiently.
- Cross-Language. Works with languages like JavaScript, Java, Python, Ruby, and C# via language-specific plugins.
These characteristics of gauge specifications are successfully implemented into Testomat.io, where they are managed.
Data-Driven Testing
Data-driven testing in Gauge enhances test coverage and efficiency, making it ideal for teams aiming to validate complex application behaviors across varied inputs while keeping specifications clear and maintainable. Data-Driven Testing in Gauge is a testing approach where test cases are executed with multiple sets of input data to validate different scenarios without duplicating test logic.
When used with a test management system testomat.io, Gauge’s data-driven tests can be imported, executed, and tracked. Results from multiple data sets are aggregated into reports, highlighting pass/fail trends and key metrics, which can be exported as PDFs for stakeholder communication.
Gauge Re-using Steps
Gauge promotes the reuse of test steps to create modular, maintainable, and readable test specifications. This reduces redundancy, simplifies test maintenance, and ensures consistency across test cases, enabling teams to focus on application behavior rather than repetitive scripting. Re-using steps equally is implemented into testomat.io with the Step Database and autocompletion functionality.
Gauge vs Cucumber
Gauge is not strictly a BDD framework, but it can be used in a BDD-like approach depending on how your team applies it. Gauge is better described as a specification-driven testing framework. Unlike Cucumber, Gauge uses simple Markdown for writing test specifications (instead of Gherkin). Focuses more on acceptance testing and readable test documentation than rigid Given/When/Then structure.
How the Gauge Test Management Integration works?
Gauge framework support provides additional flexibility for QA teams using Gauge, reduces manual linking and tracking, and enhances consistency in automated test reporting during CI\CD. The integration includes a full setup guide — commands and configuration steps are available in test management UI hints — so getting Gauge reporting working is straightforward, just like with other supported frameworks, like Cypress, Playwright, Cucumber, CodeceptJS, e.g.
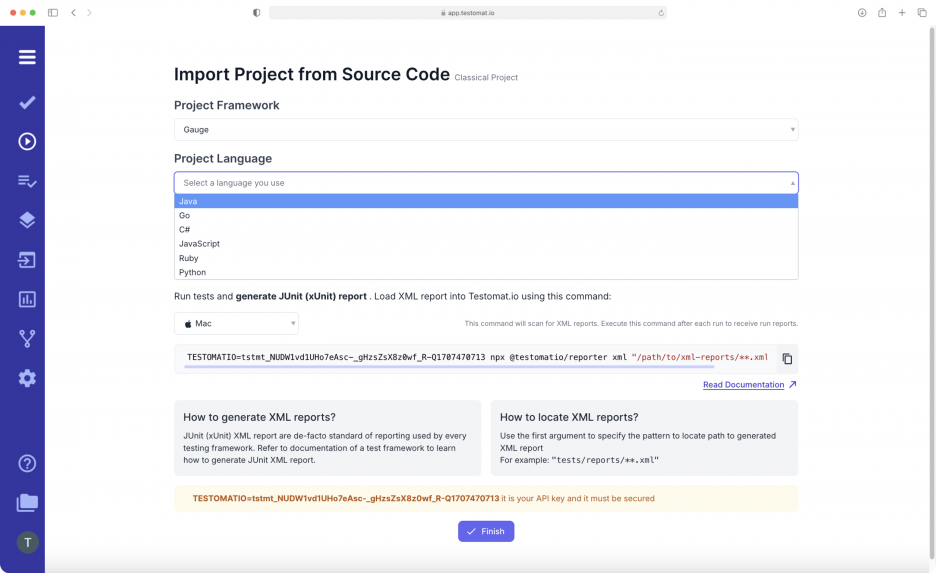
Import Test Project from Source Code
- Select the desired framework: Gauge
- Project Language: Java, Go, C#, JavaScript, Ruby, Python
- ОС: Mac, Linux Windows most likely, it will be picked automatically.
- Update test IDs so that Gauge tests stay properly linked to the right test cases
*When importing manual Gauge BDD test cases, select the Markdown import option.
After setting the necessary parameters, all the tests previously created in Gauge can be transferred to the test management system with a single click of the Finish button and will be available in our test management system.
Gauge Test Automation Report
- Report Automated tests in the drop-down Menu
- Install the test management reporting Plugin in the .conf file
- Follow UI hints provided for the command line
Ready Run Result Report use on your own or share with stakeholders as a Public report, PDF format or via email.
Gauge Test Management Benefits
- Unified test management allows centralization of Gauge scenarios and steps in one test case repository, simplifying test organization and oversight. It is like a bridge between code and test management.
- Improved traceability. Linking Gauge scenarios to requirements or user stories, ensuring full traceability for audits and compliance.
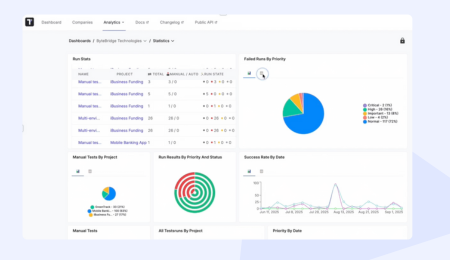
- Customizable Reporting, our test management tool provides professional reports enabling teams to generate rich reports that present Gauge test outcomes — testing progress, error details, not only fail or pass statuses, but also detailed explanations within stack traces and exceptions. Maintaining historical records for retrospective analysis during sprint cycles. The Advanced Analytics Dashboard highlight key metrics and trends.
- Enhanced shareability. It is easy to share insights during sprint reviews, release planning, or audits.
- CI\CD Integration connects Gauge test runs with CI\CD pipelines (e.g., Jenkins, GitHub Actions) to trigger automated tests and sync results back to Testomat.io.
- Streamlined Collaboration. Team members can assign tasks and link Gauge test results to project milestones, enhancing visibility and reducing miscommunication.
Associated Gauge tests features pipeline
- Detached Status – in test cases, you can not only make changes but also remove them from the code when they are not needed or by mistake. In this case, we can’t do without a kind of synchronization as well. Detached status functionality prevents test divergence between the testing framework and test management system. Its essence is that if a test is not found during the next import, it is marked as Detached. The QA engineer can verify changes in the project and either accept them or cancel the deletion.
- Out-of-sync test cases – the Out of Sync function allows comparing the test scenario after modifying it with the previous imported version. If there is a discrepancy between them, the test scenario is marked as Out of Sync. To make the test scenario up-to-date, you need to import it again.
- Living Docs – living documentation is technical project documentation generated automatically in a simple way. This allows all project participants to work with it: not only testers with specific knowledge and skills but also all interested parties. It is automatically updated with every change you make to the system, including after importing BDD tests or changing feature files via Feature editing mode.