Gaming Software Testing Management: A Practical Guide to Quality Assurance in Game Development
The Game Development Market is to reach USD $3.87B by 2031, but a single bug-filled release can sink years of development work. Unlike traditional software testing, game testing requires checking not just functionality but also player experience, performance under stress, and compatibility across dozens of devices. This guide explains how modern test management systems handle the unique demands of game development.
What is the game testing process?
Game testing starts long before the first playable build. During pre-production, quality assurance teams test core mechanics to verify they work as intended. As development progresses through alpha and beta phases, testing becomes more complex. A testing team might run thousands of test cases checking everything from collision detection to save file integrity. The testing process typically follows these phases:
- Early development testing focuses on individual game elements. Testers verify that basic controls respond correctly and that the game engine handles fundamental operations without crashing.
- Alpha testing examines how different game systems interact. Does the inventory system work with the crafting system? Can players access all intended areas of the map? Testing at this stage often reveals logic errors that only surface when multiple features combine.
- Beta testing brings in external players to stress-test the game under real-world conditions. This phase catches issues that internal testers miss because they know the game too well to stumble into edge cases that confuse new players.
- Regression testing happens continuously throughout development. Every time developers fix a bug or add content, testers must verify that these changes didn’t break existing functionality. A modern game might require 50,000+ regression test cases.
What are the types of game testing?
Game studios use multiple testing approaches, each targeting specific aspects of the game. Knowing these different types helps teams allocate resources effectively and catch problems that single-method testing would miss.
| Testing Type | Purpose | When Applied |
| Unit testing | Verify individual code functions | Throughout development |
| Functional testing | Check features work as designed | Alpha phase onward |
| Regression testing | Ensure changes don’t break existing features | After every significant change |
| Performance testing | Measure frame rates and resource usage | Beta phase and optimization |
| Load testing | Test server capacity and stability | Multiplayer games, stress scenarios |
| Soak testing | Find issues from prolonged runtime | Late beta, focused on stability |
| Compatibility testing | Verify operation across devices/platforms | Throughout, intensified at beta |
| Exploratory testing | Creative bug hunting without scripts | All phases, especially after milestones |
| Beta testing | External player feedback | Pre-release phase |
| Compliance testing | Meet platform manufacturer requirements | Console games, pre-submission |
What are the key challenges faced by game testers?
Game studios often face tight deadlines. When a game enters crunch time before release, the testing team must evaluate late-added features without delay. This pressure can lead to missed bugs if test management isn’t efficient.
Testing complexity in modern game titles
Today’s games feature complex AI systems, physics engines, procedural generation, and interconnected online features. A single game might require unit testing of individual functions, integration testing of subsystems, and end-to-end testing of complete player experiences.
Device fragmentation for mobile game testing
Mobile game testers face particular challenges. An iOS game must work across iPhone and iPad models spanning several years, each with different capabilities. Android fragmentation is worse, with thousands of device models. Testing may require automation to cover enough configurations.
Multiplayer testing requirements
Testing multiplayer features means coordinating multiple testers simultaneously. How does the game handle connection drops? What happens when players exploit mechanics not intended by game developers? Multiplayer testing requires specialized tools and significant coordination.
How do game testers work in the game development life cycle?
Game testers are responsible for more than finding bugs. They provide feedback on game design issues, suggest usability improvements, and document every problem with enough detail that developers can recreate and fix it.
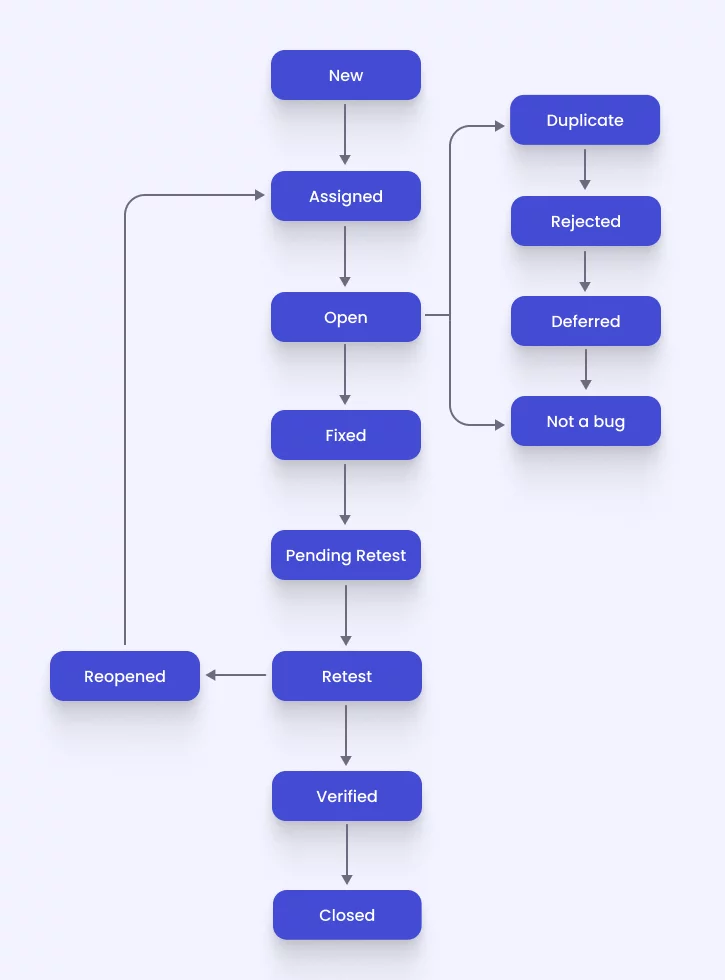
A typical bug report includes:
- Steps to reproduce the issue
- Expected versus actual behavior
- Screenshots or video capture
- System specifications
- Build number and test environment
Game testers need strong communication skills to explain complex technical problems to programmers and designers. They must understand game production workflows and adapt their testing approach as development priorities shift.
🔎 Read also: 19 Best Report Testing Tools: Comprehensive List
What are the best game testing tools and test management systems?
Many game studios use testing tools designed for general software development, then adapt them to gaming needs. These include:
- Unit testing frameworks for verifying individual code functions
- Automation tools for regression testing
- Performance monitoring tools for tracking frame rates and resource usage
Specialized game testing tools
Some tools target gaming specifically. These handle tasks like automated gameplay capture, visual regression testing to catch graphical glitches, and specialized reporting for console certification requirements.
Modern test management platforms
Software like Testomat.io brings together manual and automated testing in one system. A comprehensive test management tool should:
- Organize test cases logically by game area, feature, or priority
- Track test execution across different environments and builds
- Generate real-time reports showing testing progress
- Integrate with CI/CD pipelines for automated test execution
- Support both manual test runs and automated test synchronization
- Provide analytics to identify flaky tests and coverage gaps
The advantage of a unified test management system is visibility. Developers see which areas have been tested. Producers track progress toward release milestones. Stakeholders access public reports without needing technical knowledge.
Test automation in game development
Software testing uses automation extensively, but automating game tests presents unique challenges. Automated tests excel at regression testing, where the same sequences run repeatedly to verify nothing broke. They struggle with aspects requiring human judgment, like whether a visual effect looks correct or if gameplay feels satisfying.
Unlike software testing in business applications, game testing often requires subjective evaluation. Automated systems can measure frame rates but can’t judge if a game is fun. This means game testing is highly dependent on skilled human testers, even in studios with strong automation.
The testing and quality assurance process benefits from a mixed approach:
- Automated tests verify technical functionality
- Manual testers evaluate user experience
- Load testing automation stresses systems
- Human testers conduct exploratory testing
What are the best practices for game testing management?
Testing shouldn’t wait until a game is nearly complete. Early testing catches design problems when they’re cheap to fix. If core mechanics don’t work in the prototype phase, better to discover that before spending months building content around them.
1️⃣ Create comprehensive test plans
Before testing begins, define what success looks like. What features are critical versus nice-to-have? Which game platforms take priority? How will you measure game quality?
2️⃣ Use test case organization effectively
Large games might have 10,000+ test cases. Without organization, testers waste time finding relevant tests. Effective systems use tags, hierarchies, and search functions to help testers quickly locate needed test cases.
3️⃣ Track metrics that matter
Important metrics include:
- Test coverage percentage
- Defect density (bugs per 1000 lines of code)
- Average time to fix bugs
- Percentage of tests passing per build
- Critical bugs remaining before release
Analytics dashboards that track these metrics help teams make data-driven decisions about when a game is ready to ship.
4️⃣ Document the testing experience
Testing documentation serves multiple purposes. It helps new team members understand test strategy. It provides developers with context when bugs are reported. It creates institutional knowledge so teams don’t repeat past mistakes.
5️⃣ Enable collaboration between testers and developers
The best game studios treat testers as full team members, not just bug finders. When testers understand why developers made certain choices, they provide better feedback. When developers respect tester expertise, they fix issues more effectively.
What is the best test management for different game types?
Console manufacturers require extensive compliance testing. Games must meet dozens of technical requirements covering controller inputs, system messages, save data management, and more. Failing certification delays release and costs money. Experienced testing teams maintain detailed checklists for each platform.
Mobile game considerations
Mobile games face constant OS updates that can break functionality. Testing pipelines need to verify new Android and iOS versions quickly. Mobile game testing also requires checking touch controls, battery usage, and behavior during phone calls or notifications.
PC game complexity
PC games need testing across various graphics cards, processors, display resolutions, and peripheral devices. The variety makes comprehensive testing challenging without proper test management.
Testing for different game engines
Popular game engines like Unity and Unreal provide built-in testing frameworks. Effective test management integrates these tools while adding organization and reporting layers that engines don’t provide natively.
What is the role of AI in modern game testing?
AI testing tools can generate test cases automatically by analyzing game code and design documents. They can predict which areas are most likely to have bugs based on code complexity. Some tools even play games autonomously to discover issues.
However, AI currently supplements rather than replaces human testers. AI can execute repetitive tests faster but struggles with nuanced problems. A human tester notices when game pacing feels wrong or when dialogue seems unnatural. These qualitative assessments remain crucial parts of game quality assurance.
⏯️ Learn more about AI-powered testing in a video from an industry expert: Expert Talk on AI in Testing – Jason Arbon
Integration with modern development practices
Modern game production increasingly adopts continuous integration practices. Every code commit triggers automated test runs. Test management systems that integrate with CI/CD tools provide immediate feedback to developers, catching problems before they reach main branches.
Supporting agile game development
Agile methodologies are common in game development. Testing must keep pace with rapid iteration cycles. This requires flexible test plans that accommodate changing requirements and priorities.
Remote and distributed testing teams
Many studios now have distributed teams across time zones. Cloud-based test management systems enable coordination without everyone being physically present. Testers in different locations can access the same test cases, see real-time execution status, and collaborate on complex issues.
How to measure testing success in game development?
A game is released not when testing finds zero bugs but when remaining bugs are minor enough that they won’t significantly impact player experience. Testing ensures that the game meets quality standards while staying on schedule and within budget.
Key indicators of successful test management include:
- Low critical bug count at release
- Minimal day-one patches needed
- Positive player reception regarding stability
- Efficient use of testing resources
- Clear communication between all teams
Looking ahead
Game complexity continues to increase. Live service games receive constant updates requiring ongoing testing. Cross-platform play means ensuring consistent experience whether players use PC, console, or mobile devices. Virtual reality and cloud gaming introduce new testing dimensions.
Effective test management becomes more important as games grow more ambitious. Studios that invest in proper QA infrastructure, including modern test management systems, skilled testers, and smart automation, consistently ship higher-quality games.
The game development process demands rigorous testing at every stage. From initial concept through post-release support, comprehensive quality assurance protects both player satisfaction and studio reputation. Test management systems that organize this complexity while providing visibility to all stakeholders have become essential tools in modern game production.
Frequently asked questions
How do I choose the right test management system for my game studio?

Assess your workflow and scale first. Small studios need simple systems handling both manual and automated tests. Look for native integrations with your existing tools like Jira, Jenkins, or Slack. Test migration ease from TestRail or CSV files. Platforms like Testomat.io offer free plans for small teams, scaling to enterprise AI features.
What's the difference between traditional software testing tools and game-specific test management?

Traditional software testing checks functionality only. Game testing requires subjective quality assessment, does movement feel responsive, are explosions impressive? Games need platform-specific testing (console requirements, mobile interruptions, PC hardware variations) and handle unpredictable player behavior requiring more exploratory testing than business software’s linear workflows.
How can test management improve our game's time to market?

Organized testing catches bugs earlier when fixes cost less. Centralized platforms eliminate redundant testing and show coverage gaps. CI/CD integration provides immediate feedback, preventing bug accumulation. Analytics prioritize high-defect areas. Teams report 30-40% fewer escaped bugs and 20-25% faster regression cycles with proper test management.
What level of test automation should we implement for our game projects?

Automate 40-60% for regression tests, smoke tests, compatibility checks, and performance benchmarks. Keep manual testing for exploratory work, user experience evaluation, and visual quality. Mobile games need higher automation due to frequent updates. Testomat.io syncs automated tests from code while supporting manual cases with unified reporting.